Synergistic Hydrolysis of Cellulose by a Blend of Cellulase-Mimicking Polymeric Nanoparticle Catalysts
- PMID: 36069714
- PMCID: PMC10183977
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c06848
Synergistic Hydrolysis of Cellulose by a Blend of Cellulase-Mimicking Polymeric Nanoparticle Catalysts
Abstract
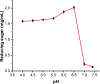
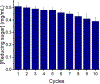
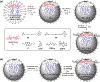
Enzyme-like catalysts by design have been a long sought-after goal of chemists but difficult to realize due to the challenges in the construction of multifunctionalized active sites with accurately positioned catalytic groups for complex substrates. Hydrolysis of cellulose is a key step in biomass utilization and requires multiple enzymes to work in concert to overcome the difficulty associated with hydrolyzing the recalcitrant substrate. We here report methods to construct synthetic versions of these enzymes through covalent molecular imprinting and strategic postmodification of the imprinted sites. The synthetic catalysts cleave a cellulose chain endolytically at multiple positions or exolytically from the nonreducing end by one or three glucose units at a time, all using the dicarboxylic acid motif found in natural cellulases. By mimicking the endocellulase, exocellulase, and β-glucosidase, the synthetic catalysts hydrolyze cellulose in a synergistic manner, with an activity at 90 °C in pH 6.5 buffer more than doubled that of Aspergillus niger cellulase at pH 5 and 37 °C and 44% of that of a commercial cellulase blend (from Novozyme). As robust cross-linked polymeric nanoparticles, the synthetic catalysts showed little changes in activity after preheating at 90 °C for 3 days and could be reused, maintaining 76% of activity after 10 reaction cycles.
Figures







References
-
- Himmel ME; Ding S-Y; Johnson DK; Adney WS; Nimlos MR; Brady JW; Foust TD Biomass Recalcitrance: Engineering Plants and Enzymes for Biofuels Production. Science 2007, 315, 804–807. - PubMed
-
- Huber GW; Iborra S; Corma A Synthesis of Transportation Fuels from Biomass: Chemistry, Catalysts, and Engineering. Chem. Rev 2006, 106, 4044–4098. - PubMed
-
- Luterbacher JS; Rand JM; Alonso DM; Han J; Youngquist JT; Maravelias CT; Pfleger BF; Dumesic JA Nonenzymatic Sugar Production from Biomass Using Biomass-Derived Γ-Valerolactone. Science 2014, 343, 277–280. - PubMed
-
- Luterbacher JS; Martin Alonso D; Dumesic JA Targeted Chemical Upgrading of Lignocellulosic Biomass to Platform Molecules. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4816–4838.
-
- Robertson GP; Hamilton SK; Barham BL; Dale BE; Izaurralde RC; Jackson RD; Landis DA; Swinton SM; Thelen KD; Tiedje JM Cellulosic Biofuel Contributions to a Sustainable Energy Future: Choices and Outcomes. Science 2017, 356, eaal2324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

