Reassessment of Historical Clinical Trials Supports the Effectiveness of Phage Therapy
- PMID: 36069758
- PMCID: PMC9769689
- DOI: 10.1128/cmr.00062-22
Reassessment of Historical Clinical Trials Supports the Effectiveness of Phage Therapy
Abstract
Phage therapy has become a hot topic in medical research due to the increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria strains. In the treatment of bacterial infections, bacteriophages have several advantages over antibiotics, including strain specificity, lack of serious side effects, and low development costs. However, scientists dismissed the clinical success of early clinical trials in the 1940s, slowing the adoption of this promising antibacterial application in Western countries. The current study used statistical methods commonly used in modern meta-analysis to reevaluate early 20th-century studies and compare them with clinical trials conducted in the last 20 years. Using a random effect model, the development of disease after treatment with or without phages was measured in odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Based on the findings of 17 clinical trials conducted between 1921 and 1940, phage therapy was effective (OR = 0.21, 95% CI = 0.10 to 0.44, P value < 0.0001). The current study includes a topic review on modern clinical trials; four could be analyzed, indicating a noneffective therapy (OR = 2.84, 95% CI = 1.53 to 5.27, P value = 0.0009). The results suggest phage therapy was surprisingly less effective than standard treatments in resolving bacterial infections. However, the results were affected by the small sample set size. This work also contextualizes the development of phage therapy in the early 20th century and highlights the expansion of phage applications in the last few years. In conclusion, the current review shows phage therapy is no longer an underestimated tool in the treatment of bacterial infections.
Keywords: Felix d’Hérelle; bacteriophage therapy; clinical trials; effectiveness; historical evaluation; history of science; meta-analysis; phage therapy; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
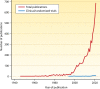


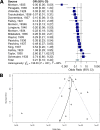
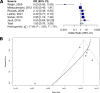
References
-
- Cassini A, Högberg LD, Plachouras D, Quattrocchi A, Hoxha A, Simonsen GS, Colomb-Cotinat M, Kretzschmar ME, Devleesschauwer B, Cecchini M, Ouakrim DA, Oliveira TC, Struelens MJ, Suetens C, Monnet DL, Strauss R, Mertens K, Struyf T, Catry B, Latour K, Ivanov IN, Dobreva EG, Tambic Andraševic A, Soprek S, Budimir A, Paphitou N, Žemlicková H, Schytte Olsen S, Wolff Sönksen U, Märtin P, Ivanova M, Lyytikäinen O, Jalava J, Coignard B, Eckmanns T, Abu Sin M, Haller S, Daikos GL, Gikas A, Tsiodras S, Kontopidou F, Tóth Á, Hajdu Á, Guólaugsson Ó, Kristinsson KG, Murchan S, Burns K, Pezzotti P, Gagliotti C, Dumpis U, et al. 2019. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: a population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 19:56–66. 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30605-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

