Radiation-induced Cell Death and Its Mechanisms
- PMID: 36069830
- PMCID: PMC9512240
- DOI: 10.1097/HP.0000000000001601
Radiation-induced Cell Death and Its Mechanisms
Abstract
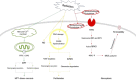
With rapid technical advances, ionizing radiation has been put into wider application in ordinary living, with the worst cytological effect on the human body being cell death. Moreover, according to the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death, the method of radiation-induced cell death, usually classified as interphase and proliferative death, undergoes more detailed classifications oriented by its molecular mechanism. Elaborating its mode and molecular mechanism is crucial for the protection and treatment of radiation injury, as well as the radiotherapy and recovery of tumors. Varying with the changes of the radiation dose and the environment, the diverse targets and pathways of ionizing radiation result in various cell deaths. This review focuses on classifications of radiation-induced cell death and its molecular mechanism. We also examine the main characteristics of ionizing radiation-induced cell death. The modes of radiation-induced cell death can be classified as apoptosis, necrosis, autophagy-dependent cell death, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, immunogenic cell death, and non-lethal processes. Once the dose is high enough, radiation effects mostly appear as destructiveness ("destructiveness" is used to describe a situation in which cells do not have the opportunity to undergo a routine death process, in which case high-dose radiation works like a physical attack). This breaks up or even shatters cells, making it difficult to find responses of the cell itself. Due to diversities concerning cell phenotypes, phases of cell cycle, radiation dose, and even cellular subregions, various methods of cell death occur, which are difficult to identify and classify. Additionally, the existence of common initial activation and signaling molecules among all kinds of cell deaths, as well as sophisticated crossways in cellular molecules, makes it more laborious to distinguish and classify various cell deaths.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the Health Physics Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Yunfei Jiao and Fangyu Cao contributed equally to the preparation of this paper. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Akpolat M, Oz ZS, Gulle K, Hamamcioglu AC, Bakkal BH, Kececi M. X irradiation induced colonic mucosal injury and the detection of apoptosis through PARP-1/p53 regulatory pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 127:110134; 2020. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhry MA. Radiation-induced microRNA: discovery, functional analysis, and cancer radiotherapy. J Cell Biochem 115:436–449; 2014. - PubMed
-
- Chaurasia M, Bhatt AN, Das A, Dwarakanath BS, Sharma K. Radiation-induced autophagy: mechanisms and consequences. Free Radic Res 50:273–290; 2016. - PubMed
-
- Contassot E, Gaide O, French LE. Death receptors and apoptosis. Dermatol Clin 25:487–501; 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

