Homoatomic cations: From [P5]+ to [P9]
- PMID: 36070385
- PMCID: PMC9451154
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abq8613
Homoatomic cations: From [P5]+ to [P9]
Abstract
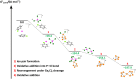
Recent synthetic approaches to a series of [P9]X salts (X = [F{Al(ORF)3}2], [Al(ORF)4], and (RF = C(CF3)3); Ga2Cl7) overcome limitations in classical synthesis methods that proved unsuitable for phosphorus cations. These salts contain the homopolyatomic cation [P9]+ via (I) oxidation of P4 with NO[F{Al(ORF)3}2], (II) the arene-stabilized Co(I) sandwich complex [Co(arene)2][Al(ORF)4] [arene = ortho-difluorobenzene (o-DFB) and fluorobenzene (FB)], or (III) the reduction of [P5Cl2][Ga2Cl7] with Ga[Ga2Cl7] as Ga(I) source in the presence of P4. Quantum chemical CCSD(T) calculations suggest that [P9]+ formation from [Co(arene)2]+ occurs via the nido-type cluster [(o-DFB)CoP4]+, which resembles the isoelectronic, elusive [P5]+. Apparently, the nido-cation [P5]+ forms intermediately in all reactions, particularly during the Ga(I)-induced reduction of [P5Cl2]+ and the subsequent pick up of P4 to yield the final salt [P9][Ga2Cl7]. The solid-state structure of [P9][Ga2Cl7] reveals the anticipated D2d-symmetric Zintl-type cage for the [P9]+ cation. Our approaches show great potential to bring other [Pn]+ cations from the gas to the condensed phase.
Figures


References
-
- Gillespie R. J., Passmore J., Polycations of group VI. Acc. Chem. Res. 4, 413–419 (1971).
-
- Bartlett N., Lohmann D. H., Fluorides of the noble metals. Part II. Dioxygenyl hexafluoroplatinate(V), O2+[PtF6]−. J. Chem. Soc. 1962, 5253–5261 (1962).
-
- Bartlett N., Lohmann D. H., Dioxygenyl hexafluoroplatinate(V) O2+[PtF6]−. Proc. Chem. Soc., 115–116 (1962).
-
- Ballone P., Jones R. O., Density functional study of phosphorus and arsenic clusters using local and nonlocal energy functionals. J. Chem. Phys. 100, 4941–4946 (1994).
-
- Martin T. P., Compound clusters. Z. Phys. D. 3, 211–217 (1986).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

