On-demand, remote and lossless manipulation of biofluid droplets
- PMID: 36070425
- PMCID: PMC9634865
- DOI: 10.1039/d2mh00695b
On-demand, remote and lossless manipulation of biofluid droplets
Abstract
The recent global outbreaks of epidemics and pandemics have shown us that we are severely under-prepared to cope with infectious agents. Exposure to infectious agents present in biofluids (e.g., blood, saliva, urine etc.) poses a severe risk to clinical laboratory personnel and healthcare workers, resulting in hundreds of millions of hospital-acquired and laboratory-acquired infections annually. Novel technologies that can minimize human exposure through remote and automated handling of infectious biofluids will mitigate such risk. In this work, we present biofluid manipulators, which allow on-demand, remote and lossless manipulation of virtually any liquid droplet. Our manipulators are designed by integrating thermo-responsive soft actuators with superomniphobic surfaces. Utilizing our manipulators, we demonstrate on-demand, remote and lossless manipulation of biofluid droplets. We envision that our biofluid manipulators will not only reduce manual operations and minimize exposure to infectious agents, but also pave the way for developing inexpensive, simple and portable robotic systems, which can allow point-of-care operations, particularly in developing nations.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
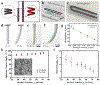


References
-
- Pike RM, Laboratory-associated infections: incidence, fatalities, causes, and prevention. Annu. Rev. Microbiol 1979, 33 (1), 41–66. - PubMed
-
- Organization, W. H., Health care-associated infections fact sheet. World Health Organization; 2015, 4.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

