Randomized Trial of Metformin, Ivermectin, and Fluvoxamine for Covid-19
- PMID: 36070710
- PMCID: PMC9945922
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2201662
Randomized Trial of Metformin, Ivermectin, and Fluvoxamine for Covid-19
Abstract
Background: Early treatment to prevent severe coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) is an important component of the comprehensive response to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic.
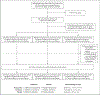
Methods: In this phase 3, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial, we used a 2-by-3 factorial design to test the effectiveness of three repurposed drugs - metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine - in preventing serious SARS-CoV-2 infection in nonhospitalized adults who had been enrolled within 3 days after a confirmed diagnosis of infection and less than 7 days after the onset of symptoms. The patients were between the ages of 30 and 85 years, and all had either overweight or obesity. The primary composite end point was hypoxemia (≤93% oxygen saturation on home oximetry), emergency department visit, hospitalization, or death. All analyses used controls who had undergone concurrent randomization and were adjusted for SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and receipt of other trial medications.
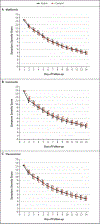
Results: A total of 1431 patients underwent randomization; of these patients, 1323 were included in the primary analysis. The median age of the patients was 46 years; 56% were female (6% of whom were pregnant), and 52% had been vaccinated. The adjusted odds ratio for a primary event was 0.84 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.66 to 1.09; P = 0.19) with metformin, 1.05 (95% CI, 0.76 to 1.45; P = 0.78) with ivermectin, and 0.94 (95% CI, 0.66 to 1.36; P = 0.75) with fluvoxamine. In prespecified secondary analyses, the adjusted odds ratio for emergency department visit, hospitalization, or death was 0.58 (95% CI, 0.35 to 0.94) with metformin, 1.39 (95% CI, 0.72 to 2.69) with ivermectin, and 1.17 (95% CI, 0.57 to 2.40) with fluvoxamine. The adjusted odds ratio for hospitalization or death was 0.47 (95% CI, 0.20 to 1.11) with metformin, 0.73 (95% CI, 0.19 to 2.77) with ivermectin, and 1.11 (95% CI, 0.33 to 3.76) with fluvoxamine.
Conclusions: None of the three medications that were evaluated prevented the occurrence of hypoxemia, an emergency department visit, hospitalization, or death associated with Covid-19. (Funded by the Parsemus Foundation and others; COVID-OUT ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT04510194.).
Copyright © 2022 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Time to Stop Using Ineffective Covid-19 Drugs.N Engl J Med. 2022 Aug 18;387(7):654-655. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2209017. N Engl J Med. 2022. PMID: 36070715 No abstract available.
-
Trial of Metformin, Ivermectin, and Fluvoxamine for Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2022 Dec 15;387(24):e65. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2212542. N Engl J Med. 2022. PMID: 36516099 No abstract available.
-
Trial of Metformin, Ivermectin, and Fluvoxamine for Covid-19. Reply.N Engl J Med. 2022 Dec 15;387(24):e65. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2212542. N Engl J Med. 2022. PMID: 36516100 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ferdinands JM, Rao S, Dixon BE, et al. Waning 2-dose and 3-dose effectiveness of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19-associated emergency department and urgent care encounters and hospitalizations among adults during periods of delta and omicron variant predominance — VISION Network, 10 states, August 2021–January 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2022;71:255–63. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thompson MG, Natarajan K, Irving SA, et al. Effectiveness of a third dose of mRNA vaccines against COVID-19-associated emergency department and urgent care encounters and hospitalizations among adults during periods of delta and omicron variant predominance — VISION Network, 10 states, August 2021–January 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2022;71:139–45. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- K23 DK124654/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK048520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002494/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR002494/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002489/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK123878/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007741/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL133604/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK124654-01A1/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK124723/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR002492/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA254849/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- KL2TR002492/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA210190/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
