Chronic back pain sub-grouped via psychosocial, brain and physical factors using machine learning
- PMID: 36071092
- PMCID: PMC9452567
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-19542-5
Chronic back pain sub-grouped via psychosocial, brain and physical factors using machine learning
Abstract
Chronic back pain (CBP) is heterogenous and identifying sub-groups could improve clinical decision making. Machine learning can build upon prior sub-grouping approaches by using a data-driven approach to overcome clinician subjectivity, however, only binary classification of pain versus no-pain has been attempted to date. In our cross-sectional study, age- and sex-matched participants with CBP (n = 4156) and pain-free controls (n = 14,927) from the UkBioBank were included. We included variables of body mass index, depression, loneliness/social isolation, grip strength, brain grey matter volumes and functional connectivity. We used fuzzy c-means clustering to derive CBP sub-groups and Support Vector Machine (SVM), Naïve Bayes, k-Nearest Neighbour (kNN) and Random Forest classifiers to determine classification accuracy. We showed that two variables (loneliness/social isolation and depression) and five clusters were optimal for creating sub-groups of CBP individuals. Classification accuracy was greater than 95% for when CBP sub-groups were assessed only, while misclassification in CBP sub-groups increased to 35-53% across classifiers when pain-free controls were added. We showed that individuals with CBP could sub-grouped and accurately classified. Future research should optimise variables by including specific spinal, psychosocial and nervous system measures associated with CBP to create more robust sub-groups that are discernible from pain-free controls.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
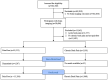
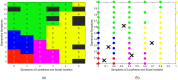
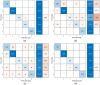
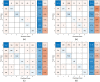
References
-
- Vos T, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390:1211–1259. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

