A RORγt+ cell instructs gut microbiota-specific Treg cell differentiation
- PMID: 36071167
- PMCID: PMC9908423
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05089-y
A RORγt+ cell instructs gut microbiota-specific Treg cell differentiation
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: A RORγt+ cell instructs gut microbiota-specific Treg cell differentiation.Nature. 2022 Oct;610(7931):E7. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05358-w. Nature. 2022. PMID: 36151471 No abstract available.
Abstract
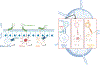
The mutualistic relationship of gut-resident microbiota and the host immune system promotes homeostasis that ensures maintenance of the microbial community and of a largely non-aggressive immune cell compartment1,2. The consequences of disturbing this balance include proximal inflammatory conditions, such as Crohn's disease, and systemic illnesses. This equilibrium is achieved in part through the induction of both effector and suppressor arms of the adaptive immune system. Helicobacter species induce T regulatory (Treg) and T follicular helper (TFH) cells under homeostatic conditions, but induce inflammatory T helper 17 (TH17) cells when induced Treg (iTreg) cells are compromised3,4. How Helicobacter and other gut bacteria direct T cells to adopt distinct functions remains poorly understood. Here we investigated the cells and molecular components required for iTreg cell differentiation. We found that antigen presentation by cells expressing RORγt, rather than by classical dendritic cells, was required and sufficient for induction of Treg cells. These RORγt+ cells-probably type 3 innate lymphoid cells and/or Janus cells5-require the antigen-presentation machinery, the chemokine receptor CCR7 and the TGFβ activator αv integrin. In the absence of any of these factors, there was expansion of pathogenic TH17 cells instead of iTreg cells, induced by CCR7-independent antigen-presenting cells. Thus, intestinal commensal microbes and their products target multiple antigen-presenting cells with pre-determined features suited to directing appropriate T cell differentiation programmes, rather than a common antigen-presenting cell that they endow with appropriate functions.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
D.R.L. consults and has equity interest in Chemocentryx, Vedanta, Immunai and Pfizer Pharmaceuticals. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







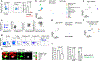

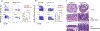
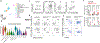


Comment in
-
A new tolerogenic cell RORs onto the scene.Sci Immunol. 2022 Oct 14;7(76):eadf0767. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adf0767. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Sci Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36206352
-
How regulatory T cells are primed to aid tolerance of gut bacteria.Nature. 2022 Oct;610(7933):638-640. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-03368-2. Nature. 2022. PMID: 36280729 No abstract available.
-
An embarrassment of riches: RORγt+ antigen-presenting cells in peripheral tolerance.Immunity. 2022 Nov 8;55(11):1978-1980. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.10.009. Immunity. 2022. PMID: 36351372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang J, Lareau CA, Bautista JL, Gupta AR, Sandor K, Germino J, Yin Y, Arvedson MP, Reeder GC, Cramer NT, Xie F, Ntranos V, Satpathy AT, Anderson MS, Gardner JM Single-cell multiomics defines tolerogenic extrathymic Aire-expressing populations with unique homology to thymic epithelium. Sci. Immunol. 6 (2021). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

