Evaluating a therapeutic window for precision medicine by integrating genomic profiles and p53 network dynamics
- PMID: 36071176
- PMCID: PMC9452682
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-022-03872-1
Evaluating a therapeutic window for precision medicine by integrating genomic profiles and p53 network dynamics
Abstract
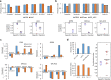
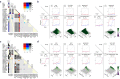
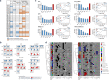
The response variation to anti-cancer drugs originates from complex intracellular network dynamics of cancer. Such dynamic networks present challenges to determining optimal drug targets and stratifying cancer patients for precision medicine, although several cancer genome studies provided insights into the molecular characteristics of cancer. Here, we introduce a network dynamics-based approach based on attractor landscape analysis to evaluate the therapeutic window of a drug from cancer signaling networks combined with genomic profiles. This approach allows for effective screening of drug targets to explore potential target combinations for enhancing the therapeutic window of drug responses. We also effectively stratify patients into desired/undesired response groups using critical genomic determinants, which are network-specific origins of variability to drug response, and their dominance relationship. Our methods provide a viable and quantitative framework to connect genotype information to the phenotypes of drug response with regard to network dynamics determining the therapeutic window.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

