Early recurrence after cryoballoon versus radiofrequency ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: mechanism and implication in long-term outcome
- PMID: 36071377
- PMCID: PMC9450458
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-022-02816-1
Early recurrence after cryoballoon versus radiofrequency ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: mechanism and implication in long-term outcome
Abstract
Background: Early recurrence (ER) after catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation (AF) has been considered as a common phenomenon but its mechanism and implication in long-term outcome has not been fully elucidated. We aimed to clarify the relation between post-ablation inflammation and ER after cryoballoon ablation (CBA) or radio-frequency ablation (RFA) and evaluate the clinical significance of ER.
Methods: A total of 154 patients with paroxysmal AF undergoing ablation were consecutively recruited, including 90 patients undergoing RFA (RF group) and 64 patients undergoing CBA (CB group). Myocardial injury and inflammation biomarkers were analyzed before and 6 h, 24 h and 48 h after ablation. Acute early recurrence (AER), non-acute early recurrence (NAER) and late recurrence (LR) was defined as recurrence of atrial tachyarrhythmia during 0-3, 4-90 days and beyond a 90-day blanking period after ablation.
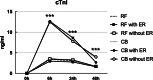
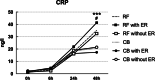
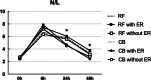
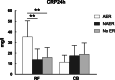
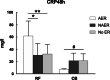
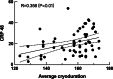
Results: Cardiac troponin I was significantly higher in CB group while C reactive protein (CRP) and Ratio Neutrophil/Lymphocyte were more elevated in RF group. Higher CRP level after RFA was significantly associated with AER in RF group and lower CRP level after CBA was predictive of AER in CB group. In addition, average cryoablation duration was positively correlated with CRP level after CB group. Cox regression revealed that NAER and left atrial diameter were associated with LR in RF group, while AER and NAER were predictive of LR after CBA.
Conclusions: Post-ablation inflammation was greater in RFA than in CBA. Excessive inflammatory response may be an important factor of AER after RFA. AER after CBA was related with lower inflammation and predictive of LR. Further investigations are still warranted to address on these findings.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Cryoballoon ablation; Early recurrence; Inflammation; Radio-frequency ablation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Yano M, Egami Y, Yanagawa K, et al. Comparison of myocardial injury and inflammation after pulmonary vein isolation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation between radiofrequency catheter ablation and cryoballoon ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2020;31(6):1315–1322. doi: 10.1111/jce.14475. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

