Masked Morphological Priming and Sensitivity to the Statistical Structure of Form-to-Meaning Mapping in L2
- PMID: 36072123
- PMCID: PMC9400631
- DOI: 10.5334/joc.221
Masked Morphological Priming and Sensitivity to the Statistical Structure of Form-to-Meaning Mapping in L2
Abstract
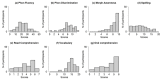
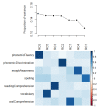
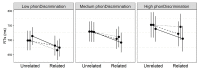
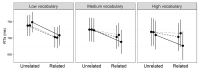
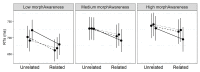
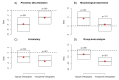
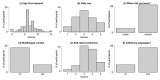
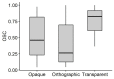
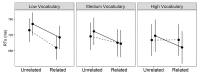
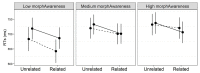
In one's native language, visual word identification is based on early morphological analysis and is sensitive to the statistical structure of the mapping between form and meaning (Orthography-to-Semantic Consistency, OSC). How these mechanisms apply to a second language is much less clear. We recruited L1 Italian-L2 English speakers for a masked priming task where the relationship between prime and target was morphologically transparent, e.g., employer-EMPLOY, morphologically opaque, e.g., corner-CORN, or merely orthographic, e.g., brothel-BROTH. Critically, participants underwent thorough testing of their lexical, morphological, phonological, spelling, and semantic proficiency in their second language. By exploring a wide spectrum of L2 proficiency, we showed that this factor critically qualifies L2 priming. Genuine morphological facilitation only arises as proficiency grows, while orthographic priming shrinks as L2 competence increases. OSC was also found to modulate priming and interact with proficiency, providing an alternative way of describing the transparency continuum in derivational morphology. Overall, these data illustrate the trajectory towards a fully consolidated L2 lexicon and show that masked priming and sensitivity to OSC are key trackers of this process.
Keywords: Bilingualism; Language proficiency; Masked priming; Morphology.
Copyright: © 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Akaike, H. (1974). A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 19, 716–723. DOI: 10.1109/TAC.1974.1100705 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

