Validation of the Social Media Disorder Scale using network analysis in a large representative sample of Czech adolescents
- PMID: 36072384
- PMCID: PMC9441909
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.907522
Validation of the Social Media Disorder Scale using network analysis in a large representative sample of Czech adolescents
Abstract
Background: The importance of studying the excessive use of social media in adolescents is increasing and so is the need for in-depth evaluations of the psychometric properties of the measurement tools. This study investigated the properties of the Social Media Disorder Scale (SMDS) in a large representative sample of Czech adolescents.
Methods: We analyzed the representative sample of 13,377 Czech adolescents (50.9% boys), 11-16 years old, who participated in the Health Behavior in School-aged Children (HBSC) survey (2017-18), using confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) and network models. Furthermore, we evaluated the measurement invariance and constructed the validity of the SMDS.
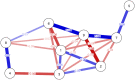
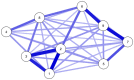
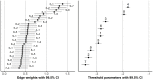
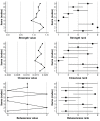
Results: We found support for a single dominant factor but not for strict unidimensionality. Several residual correlations were identified. The strongest were for: problems-conflicts-deceptions; persistence-escape; and preoccupation-tolerance-withdrawal. Girls, particularly 13- and 15-year-olds, scored higher than boys in the same age group, and 13- and 15-year-olds achieved higher scores than 11-year-olds, although some items were not invariant between the groups. The SMDS was positively related to other online activities, screen time, and falling asleep late, but negatively related to well-being and mental health.
Discussion and conclusions: The SMDS showed solid psychometric properties and construct validity. However, small violations of measurement invariance were detected. Furthermore, the network analysis showed important residual relationships between the items.
Keywords: Health Behavior in School-aged Children (HBSC); Network analysis; adolescents; problematic social media use (PSMU); psychometrics; social media addiction; validation.
Copyright © 2022 Šablatúrová, Rečka and Blinka.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Allen KA, Ryan T, Gray DL, McInerney DM, Waters L. Social media use and social connectedness in adolescents: the positives and the potential pitfalls Educ Dev Psychol. (2014) 31:18–31. 10.1017/edp.2014.2 - DOI
-
- Keles B, McCrae N, Grealish A. A systematic review: the influence of social media on depression, anxiety and psychological distress in adolescents. Int J Adolesc Youth. (2020) 25:79–93. 10.1080/02673843.2019.1590851 - DOI
-
- Müller KW, Dreier M, Beutel ME, Duven E, Giralt S, Wölfling K. A hidden type of internet addiction? Intense and addictive use of social networking sites in adolescents. Comput Hum Behav. (2016) 55:172–7. 10.1016/j.chb.2015.09.007 - DOI
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; (2013).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

