Effects of Aerosol Inhalation Combined with Intravenous Drip of Polymyxin B on Bacterial Clearance, Symptoms Improvement, and Serum Infection Indexes in Patients with Pneumonia Induced by Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria
- PMID: 36072613
- PMCID: PMC9441374
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5244538
Effects of Aerosol Inhalation Combined with Intravenous Drip of Polymyxin B on Bacterial Clearance, Symptoms Improvement, and Serum Infection Indexes in Patients with Pneumonia Induced by Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria
Abstract
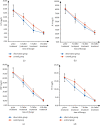
In recent years, the incidence of pneumonia caused by multidrug-resistant (MDR) Gram-negative bacteria (G-) has increased year by year. Polymyxin B has a good clinical effect in the treatment of MDR, but there is controversy about the administration route of this drug. In this study, we retrospectively analyzed the clinical data of 84 cases of MDR Gram-negative bacterial pneumonia, and aimed to explore the effects of aerosol inhalation combined with intravenous polymyxin B infusion on the bacterial clearance, symptom improvement, and serum infection indexes of MDR patients on the patients with Gram-negative (G-) bacterial pneumonia. The results show that aerosol inhalation combined with intravenous drip of polymyxin B can improve bacterial clearance rate, reduce levels of serum inflammatory factors, and improve clinical symptoms in patients with pneumonia induced by MDR G-bacteria.
Copyright © 2022 Hanlu Lin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Clinical study on intravenous combined with aerosol inhalation of polymyxin B for the treatment of pneumonia caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Apr;33(4):416-420. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20201215-00753. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 34053483 Chinese.
-
Parenteral polymyxin B use in patients with multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteremia and urinary tract infections: a retrospective case series.Ann Pharmacother. 2008 Sep;42(9):1177-87. doi: 10.1345/aph.1K346. Epub 2008 Jul 29. Ann Pharmacother. 2008. PMID: 18664609
-
Salvage treatment of pneumonia and initial treatment of tracheobronchitis caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacilli with inhaled polymyxin B.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007 Jun;58(2):235-40. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2007.01.008. Epub 2007 Mar 9. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17350201 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical use of intravenous polymyxin B for the treatment of patients with multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections: An evaluation of the current evidence.J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2021 Mar;24:342-359. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2020.12.026. Epub 2021 Jan 21. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2021. PMID: 33486122 Review.
-
Polymyxin B for the treatment of multidrug-resistant pathogens: a critical review.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007 Dec;60(6):1206-15. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkm357. Epub 2007 Sep 17. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17878146 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical outcomes and safety of polymyxin B versus tigecycline combination therapy for pneumonia of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: a retrospective cohort study.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2397087. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2397087. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39239861 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the clinical efficacy and toxicity of nebulized polymyxin monotherapy and combined intravenous and nebulized polymyxin for the treatment of ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by carbapenem-resistant gram-negative bacteria: a retrospective cohort study.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 16;14:1209063. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1209063. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37663252 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of different polymyxin-containing regimens for the treatment of pneumonia caused by multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2024 Jul 14;28(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s13054-024-05031-w. Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 39004760 Free PMC article.
-
Polymyxins: recent advances and challenges.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 21;15:1424765. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1424765. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38974043 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu Y., Li R., Xiao X., Wang Z. Antibiotic adjuvants: an alternative approach to overcome multi-drug resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Critical Reviews in Microbiology . 2019;45(3):301–314. - PubMed
-
- Michalopoulos A., Kasiakou S. K., Mastora Z., Rellos K., Kapaskelis A. M., Falagas M. E. Aerosolized colistin for the treatment of nosocomial pneumonia due to multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in patients without cystic fibrosis. Critical Care . 2005;9(1):R53–R59. doi: 10.1186/cc3020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Furtado G. H. C., D’Azevedo P. A., Santos A. F., Gales A. C., Pignatari A. C. C., Medeiros E. A. S. Intravenous polymyxin B for the treatment of nosocomial pneumonia caused by multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents . 2007;30(4):315–319. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2007.05.017. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources