Artificial Intelligence Algorithm-Based MRI in the Diagnosis of Complications after Renal Transplantation
- PMID: 36072641
- PMCID: PMC9398844
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8930584
Artificial Intelligence Algorithm-Based MRI in the Diagnosis of Complications after Renal Transplantation
Abstract
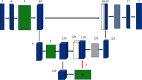
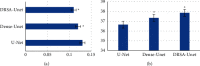
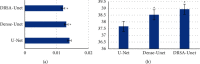
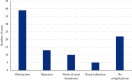
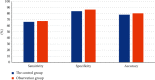
This study was to explore the diagnostic value of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) optimized by residual segmentation attention dual channel network (DRSA-U-Net) in the diagnosis of complications after renal transplantation and to provide a more effective examination method for clinic. 89 patients with renal transplantation were selected retrospectively, and all underwent MRI. The patients were divided into control group (conventional MRI image diagnosis) and observation group (MRI image diagnosis based on DRSA-U-Net). The accuracy of MRI images in the two groups was evaluated according to the comprehensive diagnostic results. The root mean square error (RMSE) and peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) of DRSA-U-Net on T1WI and T2WI sequences were better than those of U-Net and dense U-Net (P < 0.05); comprehensive examination showed that 39 patients had obstruction between ureter and bladder anastomosis, 13 cases had rejection, 10 cases had perirenal hematoma, 5 cases had renal infarction, and 22 cases had no complications; the diagnostic sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and consistency of the observation group were higher than those of the control group (P < 0.05). In the control group, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy in the diagnosis of complications after renal transplantation were 66.5%, 84.1%, and 78.32%, respectively; in the observation group, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy in the diagnosis were 67.8%, 86.7%, and 80.6%, respectively. DRSA-U-Net denoising algorithm can clearly display the information of MRI images on the kidney, ureter, and surrounding tissues, improve its diagnostic accuracy in complications after renal transplantation, and has good clinical application value.
Copyright © 2022 Hang Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ferreri A. J. M., Cwynarski K., Pulczynski E., et al. Chemoimmunotherapy with methotrexate, cytarabine, thiotepa, and rituximab (MATRix regimen) in patients with primary CNS lymphoma: results of the first randomisation of the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group-32 (IELSG32) phase 2 trial. The Lancet Haematology . 2016;3(5):217–227. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(16)00036-3. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
