Viral RNA Load in Symptomatic and Asymptomatic COVID-19 Omicron Variant-Positive Patients
- PMID: 36072643
- PMCID: PMC9444452
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5460400
Viral RNA Load in Symptomatic and Asymptomatic COVID-19 Omicron Variant-Positive Patients
Abstract
Objectives: Viral load is important when evaluating viral transmission potential, involving the use of a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) cycle threshold (Ct) value. We aimed to analyze the PCR Ct values of respiratory tract samples taken from patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron variant strains to evaluate these strains' viral dynamics.
Methods: This study comprised 361 patients. The Ct values of SARS-CoV-2-related respiratory samples were compared between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients.
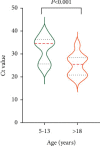
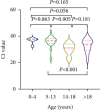
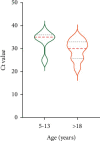
Results: The median (25th percentile and 75th percentile) nasopharynx and oropharynx SARS-CoV-2 Ct values were 30.5 (24.5-35.0) and 34.5 (30.0-37.0) in the symptomatic group, respectively, and 27.8 (23.4-34.5) and 33.5 (26.0-35.0) in the asymptomatic group, respectively, without significance. In the symptomatic group, subgroup analyses according to age showed the mean nasal Ct value for patients aged >18 years was 29.0 (23.5-34.5), which was significantly lower than that of patients aged 0-4 years and 5-13 years (36.0 (30.5-38.0) and 34.5 (31.0-39.0), respectively). The nasal Ct value for asymptomatic patients aged >18 years was 25.5 (20.9-28.4), which was significantly lower than of patients aged 5-13 years (34.5 (25.6-36.4)).
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that the viral loads of asymptomatic and symptomatic patients did not differ significantly. However, adults infected with SARS-CoV-2 had higher nasal viral loads that those of young children.
Copyright © 2022 Qian Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern . Geneva Switzerland: WHO; 2021. https://www.who.int/news/item/26-11-2021-classification-of-omicron-(b.1.... .
-
- National Institute of Infectious Diseases Disease. Active epidemiological investigation on SARS-CoV-2 infection caused by omicron variant (Pango lineage B.1.1.529) in Japan: Preliminary report on infectious period. 2022. https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/en/2019-ncov-e/10884-covid19-66-en.html .
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

