Comprehensive genome sequence analysis of the devastating tobacco bacterial phytopathogen Ralstonia solanacearum strain FJ1003
- PMID: 36072670
- PMCID: PMC9441608
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.966092
Comprehensive genome sequence analysis of the devastating tobacco bacterial phytopathogen Ralstonia solanacearum strain FJ1003
Abstract
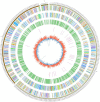
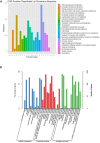
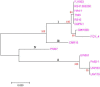
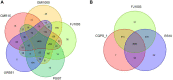
Due to its high genetic diversity and broad host range, Ralstonia solanacearum, the causative phytopathogen of the bacterial wilt (BW) disease, is considered a "species complex". The R. solanacearum strain FJ1003 belonged to phylotype I, and was isolated from the Fuzhou City in Fujian Province of China. The pathogen show host specificity and infects tobacco, especially in the tropical and subtropical regions. To elucidate the pathogenic mechanisms of FJ1003 infecting tobacco, a complete genome sequencing of FJ1003 using single-molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing technology was performed. The full genome size of FJ1003 was 5.90 Mb (GC%, 67%), containing the chromosome (3.7 Mb), megaplasmid (2.0 Mb), and small plasmid (0.2 Mb). A total of 5133 coding genes (3446 and 1687 genes for chromosome and megaplasmid, respectively) were predicted. A comparative genomic analysis with other strains having the same and different hosts showed that the FJ1003 strain had 90 specific genes, possibly related to the host range of R. solanacearum. Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) was widespread in the genome. A type Ⅲ effector protein (Rs_T3E_Hyp14) was present on both the prophage and genetic island (GI), suggesting that this gene might have been acquired from other bacteria via HGT. The Rs_T3E_Hyp14 was proved to be a virulence factor in the pathogenic process of R. solanacearum through gene knockout strategy, which affects the pathogenicity and colonization ability of R. solanacearum in the host. Therefore, this study will improve our understanding of the virulence of R. solanacearum and provide a theoretical basis for tobacco disease resistance breeding.
Keywords: Ralstonia solanacearum; Rs_T3E_Hyp14; bacterial wilt; disease resistance; effector proteins; genome sequencing; tobacco.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Zhuang, Wang, Li, Lei, Li, Gao, Wei, Dang, Raza, Yang, Sharif, Yang, Zhang, Zou and Zhuang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

