PTPA variants and impaired PP2A activity in early-onset parkinsonism with intellectual disability
- PMID: 36073231
- PMCID: PMC10115167
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awac326
PTPA variants and impaired PP2A activity in early-onset parkinsonism with intellectual disability
Abstract
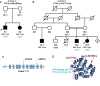
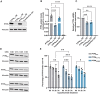
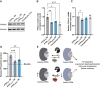
The protein phosphatase 2A complex (PP2A), the major Ser/Thr phosphatase in the brain, is involved in a number of signalling pathways and functions, including the regulation of crucial proteins for neurodegeneration, such as alpha-synuclein, tau and LRRK2. Here, we report the identification of variants in the PTPA/PPP2R4 gene, encoding a major PP2A activator, in two families with early-onset parkinsonism and intellectual disability. We carried out clinical studies and genetic analyses, including genome-wide linkage analysis, whole-exome sequencing, and Sanger sequencing of candidate variants. We next performed functional studies on the disease-associated variants in cultured cells and knock-down of ptpa in Drosophila melanogaster. We first identified a homozygous PTPA variant, c.893T>G (p.Met298Arg), in patients from a South African family with early-onset parkinsonism and intellectual disability. Screening of a large series of additional families yielded a second homozygous variant, c.512C>A (p.Ala171Asp), in a Libyan family with a similar phenotype. Both variants co-segregate with disease in the respective families. The affected subjects display juvenile-onset parkinsonism and intellectual disability. The motor symptoms were responsive to treatment with levodopa and deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus. In overexpression studies, both the PTPA p.Ala171Asp and p.Met298Arg variants were associated with decreased PTPA RNA stability and decreased PTPA protein levels; the p.Ala171Asp variant additionally displayed decreased PTPA protein stability. Crucially, expression of both variants was associated with decreased PP2A complex levels and impaired PP2A phosphatase activation. PTPA orthologue knock-down in Drosophila neurons induced a significant impairment of locomotion in the climbing test. This defect was age-dependent and fully reversed by L-DOPA treatment. We conclude that bi-allelic missense PTPA variants associated with impaired activation of the PP2A phosphatase cause autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism with intellectual disability. Our findings might also provide new insights for understanding the role of the PP2A complex in the pathogenesis of more common forms of neurodegeneration.
Keywords: PP2A; PPP2R4; PTPA; intellectual disability; parkinsonism.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Conflict of interest statement
V.B. receives honoraria from Elsevier Ltd. for serving as co-Editor-in-Chief of Parkinsonism & Related Disorders. He also received speaking honoraria from the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society, and honoraria as Chair of the MDS International Congress Program Committee (2019–2021).
Figures

Comment in
-
PTPA variants are rare in early-onset and familial Parkinson's disease.Brain. 2023 Dec 1;146(12):e125-e127. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad244. Brain. 2023. PMID: 37448355 No abstract available.
-
PTPA variants and the risk for Parkinson's disease in diverse ancestry populations.Brain. 2023 Dec 1;146(12):e120-e124. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad247. Brain. 2023. PMID: 37467482 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, et al. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science. 1997;276:2045–2047. - PubMed
-
- Paisán-Ruíz C, Jain S, Evans EW, et al. Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson's disease. Neuron. 2004;44:595–600. - PubMed
-
- Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, et al. Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron. 2004;44:601–607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

