Upgraded imaging capabilities at the BAMline (BESSY II)
- PMID: 36073889
- PMCID: PMC9455212
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600577522007342
Upgraded imaging capabilities at the BAMline (BESSY II)
Abstract
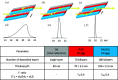
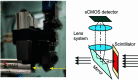
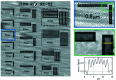
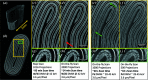
The BAMline at the BESSY II synchrotron X-ray source has enabled research for more than 20 years in widely spread research fields such as materials science, biology, cultural heritage and medicine. As a nondestructive characterization method, synchrotron X-ray imaging, especially tomography, plays a particularly important role in structural characterization. A recent upgrade of key equipment of the BAMline widens its imaging capabilities: shorter scan acquisition times are now possible, in situ and operando studies can now be routinely performed, and different energy spectra can easily be set up. In fact, the upgraded double-multilayer monochromator brings full flexibility by yielding different energy spectra to optimize flux and energy resolution as desired. The upgraded detector (based on an sCMOS camera) also allows exploiting the higher flux with reduced readout times. Furthermore, an installed slip ring allows the sample stage to continuously rotate. The latter feature enables tomographic observation of processes occurring in the time scale of a few seconds.
Keywords: X-ray optics; computed tomography; double-multilayer monochromators; pink beams; synchrotron radiation.
open access.
Figures

References
-
- Arhatari, B. D., Stevenson, A. W., Abbey, B., Nesterets, Y. I., Maksimenko, A., Hall, C. J., Thompson, D., Mayo, S. C., Fiala, T., Quiney, H. M., Taba, S. T., Lewis, S. J., Brennan, P. C., Dimmock, M., Häusermann, D. & Gureyev, T. E. (2021). Appl. Sci. 11, 4120.
-
- Arlt, T., Manke, I., Wippermann, K., Riesemeier, H., Mergel, J. & Banhart, J. (2013). J. Power Sources, 221, 210–216.
-
- Bonse, U. & Busch, F. (1996). Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 65, 133–169. - PubMed
-
- Bronnikov, A. V. (2002). J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 19, 472–480. - PubMed
-
- Buzanich, A. G., Radtke, M., Reinholz, U., Riesemeier, H. & Emmerling, F. (2016). J. Synchrotron Rad. 23, 769–776. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

