Impacts of Gestational FireMaster 550 Exposure on the Neonatal Cortex Are Sex Specific and Largely Attributable to the Organophosphate Esters
- PMID: 36075192
- PMCID: PMC9992460
- DOI: 10.1159/000526959
Impacts of Gestational FireMaster 550 Exposure on the Neonatal Cortex Are Sex Specific and Largely Attributable to the Organophosphate Esters
Abstract
Introduction: Flame retardants (FRs) are common bodily and environmental pollutants, creating concern about their potential toxicity. We and others have found that the commercial mixture FireMaster® 550 (FM 550) or its individual brominated (BFR) and organophosphate ester (OPFR) components are potential developmental neurotoxicants. Using Wistar rats, we previously reported that developmental exposure to FM 550 or its component classes produced sex- and compound-specific effects on adult socioemotional behaviors. The underlying mechanisms driving the behavioral phenotypes are unknown.
Methods: To further mechanistic understanding, here we conducted transcriptomics in parallel with a novel lipidomics approach using cortical tissues from newborn siblings of the rats in the published behavioral study. Inclusion of lipid composition is significant because it is rarely examined in developmental neurotoxicity studies. Pups were gestationally exposed via oral dosing to the dam to FM 550 or the BFR or OPFR components at environmentally relevant doses.
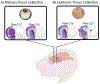
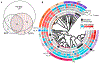
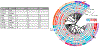
Results: The neonatal cortex was highly sexually dimorphic in lipid and transcriptome composition, and males were more significantly impacted by FR exposure. Multiple adverse modes of action for the BFRs and OPFRs on neurodevelopment were identified, with the OPFRs being more disruptive than the BFRs via multiple mechanisms including dysregulation of mitochondrial function and disruption of cholinergic and glutamatergic systems. Disrupted mitochondrial function by environmental factors has been linked to a higher risk of autism spectrum disorders and neurodegenerative disorders. Impacted lipid classes included ceramides, sphingomyelins, and triacylglycerides. Robust ceramide upregulation in the OPFR females could suggest a heightened risk of brain metabolic disease.
Conclusions: This study reveals multiple mechanisms by which the components of a common FR mixture are developmentally neurotoxic and that the OPFRs may be the compounds of greatest concern.
Keywords: Brain; Choline; DNT; Developmental neurotoxicity; Environmental toxicology; Flame retardants; ITPs IPP; Lipidomics; TPHP; TPP; Transcriptomics.
© 2022 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



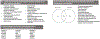


References
-
- Ma Y, Venier M, Hites RA. 2-Ethylhexyl Tetrabromobenzoate and Bis(2-ethylhexyl) Tetrabromophthalate Flame Retardants in the Great Lakes Atmosphere. Environmental Science & Technology. 2012;46(1):204–8. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Zhao L, Letcher RJ, Zhang Y, Jian K, Zhang J, et al. A review on organophosphate Ester (OPE) flame retardants and plasticizers in foodstuffs: Levels, distribution, human dietary exposure, and future directions. Environ Int. 2019;127:35–51. - PubMed

