S1-END-seq reveals DNA secondary structures in human cells
- PMID: 36075220
- PMCID: PMC9547894
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.08.007
S1-END-seq reveals DNA secondary structures in human cells
Abstract
DNA becomes single stranded (ssDNA) during replication, transcription, and repair. Transiently formed ssDNA segments can adopt alternative conformations, including cruciforms, triplexes, and quadruplexes. To determine whether there are stable regions of ssDNA in the human genome, we utilized S1-END-seq to convert ssDNA regions to DNA double-strand breaks, which were then processed for high-throughput sequencing. This approach revealed two predominant non-B DNA structures: cruciform DNA formed by expanded (TA)n repeats that accumulate in microsatellite unstable human cancer cell lines and DNA triplexes (H-DNA) formed by homopurine/homopyrimidine mirror repeats common across a variety of cell lines. We show that H-DNA is enriched during replication, that its genomic location is highly conserved, and that H-DNA formed by (GAA)n repeats can be disrupted by treatment with a (GAA)n-binding polyamide. Finally, we show that triplex-forming repeats are hotspots for mutagenesis. Our results identify dynamic DNA secondary structures in vivo that contribute to elevated genome instability.
Keywords: DNA secondary structures; END-seq; Friederichs ataxia; H-DNA; cruciforms; genome instability; mutations; non B-DNA; triplexes.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



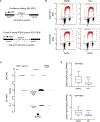

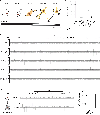
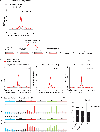
References
-
- Agazie YM, Lee JS, and Burkholder GD (1994). Characterization of a new monoclonal antibody to triplex DNA and immunofluorescent staining of mammalian chromosomes. J Biol Chem 269, 7019–7023. - PubMed
-
- Belotserkovskii BP, Mirkin SM, and Hanawalt PC (2013). DNA sequences that interfere with transcription: implications for genome function and stability. Chem Rev 113, 8620–8637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

