Antioxidant Activity of Vitis davidii Foex Seed and Its Effects on Gut Microbiota during Colonic Fermentation after In Vitro Simulated Digestion
- PMID: 36076800
- PMCID: PMC9455166
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11172615
Antioxidant Activity of Vitis davidii Foex Seed and Its Effects on Gut Microbiota during Colonic Fermentation after In Vitro Simulated Digestion
Abstract
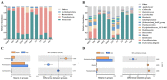
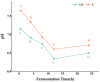
Vitis davidii Foex whole seed (VWS) is a by-product during the processing of grape products, which is rich in bioactive compounds that have great potential in the food industry. In this study, the bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of VWS were determined, and their dynamic changes during in vitro colonic fermentation were also investigated after VWS subjected to in vitro simulated digestion. Results showed that VWS were rich in polyphenols (23.67 ± 0.52 mg GAE/g), flavonoids (13.13 ± 1.22 mg RE/g), and proanthocyanidins (8.36 ± 0.14 mg CE/g). It also had good DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging activity, which reached 82.10% and 76.10% at 1000 μg/mL. The alteration trend of the antioxidant activity during in vitro fermentation for 24 h was consistent with that of the content of bioactive substances, such as polyphenols, with the extension of fermentation time. The bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity showed a trend of increasing and then decreasing, reaching the highest value at 8 h. The high-throughput sequencing analysis of the regulatory effect of VWS on intestinal micro-organisms revealed that VWS influenced intestinal microbiota diversity. The relative abundance of beneficial microbiota, such as Blautia and Parabacteroides, increased by 4.1- and 1.65-fold after 24 h of fermentation compared with that of the control group. It also reduced Escherichia-Shigella by 11.23% and effectively reduced host inflammation, while increasing the contents of acetic acid, propionic acid, and other metabolites. Taken together, these results reveal the value of VWS utilization and provide new insights into the nutritional and microbiota modulation effects of VWS, which could therefore serve as a nutraceutical ingredient in health promotion.
Keywords: Vitis davidii Foex seed; antioxidants; bioactive substances; in vitro digestion; in vitro fermentation; short-chain fatty acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest and the funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures







Similar articles
-
In vitro digestion and colonic fermentation of phenolic compounds and their antioxidant potential in Australian beach-cast seaweeds.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 22;14(1):4335. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54312-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38383637 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic Profiling and Assessment of Phenolic Compounds Derived from Vitis davidii Foex Cane and Stem Extracts.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 28;23(23):14873. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314873. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499201 Free PMC article.
-
Phenolics composition and antioxidant activity of wine produced from spine grape (Vitis davidii Foex) and Cherokee rose (Rosa laevigata Michx.) fruits from South China.J Food Sci. 2012 Jan;77(1):C8-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02499.x. Epub 2011 Dec 19. J Food Sci. 2012. PMID: 22181048
-
Effects of monoglucoside and diglucoside anthocyanins from Yan 73 (Vitis vinifera L.) and spine grape (Vitis davidii Foex) skin on intestinal microbiota in vitro.Food Chem X. 2022 Nov 7;16:100501. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2022.100501. eCollection 2022 Dec 30. Food Chem X. 2022. PMID: 36519088 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Marine Bioactive Compounds on Gut Ecology Based on In Vitro Digestion and Colonic Fermentation Models.Nutrients. 2022 Aug 12;14(16):3307. doi: 10.3390/nu14163307. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36014813 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-Index Comprehensive Assessment Optimized Critical Flavonoids Extraction from Semen Hoveniae and Their In Vitro Digestive Behavior Evaluation.Foods. 2023 Feb 10;12(4):773. doi: 10.3390/foods12040773. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36832847 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivated Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Ps-8 enhances growth performance and intestinal health in broiler chickens via gut microbiota and serum metabolite modulation.Poult Sci. 2025 Jul 26;104(10):105611. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105611. Online ahead of print. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40752195 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro digestion and colonic fermentation of phenolic compounds and their antioxidant potential in Australian beach-cast seaweeds.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 22;14(1):4335. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54312-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38383637 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of LAR1 Suppresses Anthocyanin Biosynthesis by Enhancing Catechin Competition Leading to Promotion of Proanthocyanidin Pathway in Spine Grape (Vitis davidii) Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 11;25(22):12087. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212087. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596158 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-assisted natural deep eutectic solvent extraction of anthocyanin from Vitis davidii Foex. pomace: Optimization, identification, antioxidant activity and stability.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 14;10(12):e33066. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33066. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38988524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duba K.S., Fiori L. Supercritical CO2 extraction of grape seed oil: Effect of process parameters on the extraction kinetics. J. Supercrit. Fluids. 2015;98:33–43. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2014.12.021. - DOI
-
- Hosseini-Vashan S.J., Safdari-Rostamabad M., Piray A.H., Sarir H. The growth performance, plasma biochemistry indices, immune system, antioxidant status, and intestinal morphology of heat-stressed broiler chickens fed grape (Vitis vinifera) pomace. Anim. Feed. Sci. Teth. 2020;259:11434. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2019.114343. - DOI
-
- Amorim C., Silvério S.C., Cardoso B.B., Alves J.I., Pereira M.A., Rodrigues L.R. In vitro fermentation of raffinose to unravel its potential as prebiotic ingredient. Lwt. 2020;126:109322. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109322. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

