Lactococcus garvieae FUA009, a Novel Intestinal Bacterium Capable of Producing the Bioactive Metabolite Urolithin A from Ellagic Acid
- PMID: 36076807
- PMCID: PMC9455165
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11172621
Lactococcus garvieae FUA009, a Novel Intestinal Bacterium Capable of Producing the Bioactive Metabolite Urolithin A from Ellagic Acid
Abstract
Dietary polyphenol ellagic acid has anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory activities, and these biological activities require the conversion of ellagic acid to urolithins by intestinal microbes. However, few gut microbes are capable of metabolizing ellagic acid to produce urolithins, limiting the beneficial effects of ellagic acid on health. Here, we describe an intestinal bacterium Lactococcus garvieae FUA009 isolated from the feces of a healthy volunteer. It was demonstrated via HPLC and UPLC-MS analysis that the end product of ellagic acid metabolism of FUA009 was urolithin A. In addition, we also examined the whole genome sequence of FUA009 and then assessed the safety and probiotic properties of FUA009 based on a complete genome and phenotype analysis. We indicated that FUA009 was safe, which was confirmed by FUA009 being sensitive to multiple antibiotics, having no hemolytic activity, and being free of aggressive putative virulence factors. Moreover, 19 stress-responsive protein genes and 8 adhesion-related genes were predicted in the FUA009 genome. Furthermore, we demonstrated that FUA009 was tolerant to acid and bile salt by determining the cell viability in a stress environment. In summary, Lactococcus garvieae FUA009, as a novel UA-producing bacterium, not only contributes to the study of the metabolic pathway of ellagic acid but is also expected to be a novel probiotic candidate.
Keywords: Lactococcus garvieae; complete genome; ellagic acid; plant-derived activities; safety and probiotic characteristics; urolithin A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

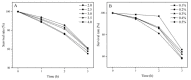
References
-
- Andreux P.A., Blanco-Bose W., Ryu D., Burdet F., Ibberson M., Aebischer P., Auwerx J., Singh A., Rinsch C. The mitophagy activator urolithin A is safe and induces a molecular signature of improved mitochondrial and cellular health in humans. Nat. Metab. 2019;1:595–603. doi: 10.1038/s42255-019-0073-4. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 32102270/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20210923/National Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- KQ20041/National Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Ocean University
- KQ20052/National Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Ocean University
- 20KJA550001/Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, the Key Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China
- SH20191204/Project"333" of Jiangsu Province, the Open-end Funds of Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Marine Bioresources and Environment
- SH20211210/Project"333" of Jiangsu Province, the Open-end Funds of Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Marine Bioresources and Environment
- JSIMR202024/Open-end Funds of Jiangsu Institute of Marine Resources Development
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

