Downregulation of miR-99b-5p and Upregulation of Nuclear mTOR Cooperatively Promotes the Tumor Aggressiveness and Drug Resistance in African American Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 36077039
- PMCID: PMC9455949
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23179643
Downregulation of miR-99b-5p and Upregulation of Nuclear mTOR Cooperatively Promotes the Tumor Aggressiveness and Drug Resistance in African American Prostate Cancer
Abstract
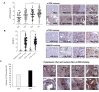
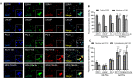
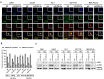
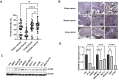
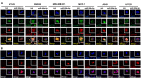
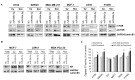
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) regulates various fundamental cellular events including cell proliferation, protein synthesis, metabolism, apoptosis, and autophagy. Tumor suppressive miR-99b-5p has been implicated in regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in a variety of types of cancer. Our previous study suggested the reciprocal miR-99b-5p/MTOR (downregulated/upregulated) pairing as a key microRNA-mRNA regulatory component involved in the prostate cancer (PCa) disparities. In this study, we further validated the expression profiles of mTOR and miR-99b-5p in the PCa, colon, breast, and lung cancer specimens and cell lines. The immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence, Western blot, and RT-qPCR assays have confirmed that mTOR is upregulated while miR-99b-5p is downregulated in different patient cohorts and a panel of cancer cell lines. Intriguingly, elevated nuclear mTOR expression was observed in African American PCa and other advanced cancers. Transfection of the miR-99b-5p mimic resulted in a significant reduction in nuclear mTOR and androgen receptor (AR), while a slight/moderate to no decrease in cytoplasmic mTOR and AR in PCa and other cancer cells, suggesting that miR-99b-5p inhibits mTOR and AR expression and their nuclear translocation. Moreover, overexpression of miR-99b-5p targets/inhibits AR-mTOR axis, subsequently initiating cell apoptosis and sensitizing docetaxel-induced cytotoxicity in various cancers. In conclusion, our data suggest that reciprocal miR-99b-5p/nuclear mTOR pairing may be a more precise diagnostic/prognostic biomarker for aggressive PCa, than miR-99b-5p/MTOR pairing or mTOR alone. Targeting the AR-mTOR axis using miR-99b-5p has also been suggested as a novel therapeutic strategy to induce apoptosis and overcome chemoresistance in aggressive PCa.
Keywords: miR-99b-5p; nuclear pmTOR; precision prognostic biomarker; reciprocal miRNA-mRNA pairing.
Conflict of interest statement
These authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Conti D.V., Darst B.V., Moss L.C., Saunders E.J., Sheng X., Chou A., Schumacher F.R., Olama A.A.A., Benlloch S., Dadaev T., et al. Trans-ancestry genome-wide association meta-analysis of prostate cancer identifies new susceptibility loci and informs genetic risk prediction. Nat. Genet. 2021;53:65–75. doi: 10.1038/s41588-020-00748-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rayford W., Beksac A.T., Alger J., Alshalalfa M., Ahmed M., Khan I., Falagario U.G., Liu Y., Davicioni E., Spratt D.E., et al. Comparative analysis of 1152 African-American and European-American men with prostate cancer identifies distinct genomic and immunological differences. Commun. Biol. 2021;4:670. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02140-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Awasthi S., Berglund A., Abraham-Miranda J., Rounbehler R.J., Kensler K., Serna A., Vidal A., You S., Freeman M.R., Davicioni E., et al. Comparative Genomics Reveals Distinct Immune-oncologic Pathways in African American Men with Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2021;27:320–329. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2925. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

