Comparative Genomic Analyses of the Genus Photobacterium Illuminate Biosynthetic Gene Clusters Associated with Antagonism
- PMID: 36077108
- PMCID: PMC9456166
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23179712
Comparative Genomic Analyses of the Genus Photobacterium Illuminate Biosynthetic Gene Clusters Associated with Antagonism
Abstract
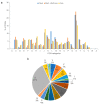
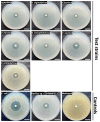
The genus Photobacterium is known for its ecophysiological versatility encompassing free-living, symbiotic, and pathogenic lifestyles. Photobacterium sp. CCB-ST2H9 was isolated from estuarine sediment collected at Matang Mangrove, Malaysia. In this study, the genome of CCB-ST2H9 was sequenced, and the pan-genome of 37 Photobacterium strains was analysed. Phylogeny based on core genes showed that CCB-ST2H9 clustered with P. galatheae, forming a distinct clade with P. halotolerans, P. salinisoli, and P. arenosum. The core genome of Photobacterium was conserved in housekeeping functions, while the flexible genome was well represented by environmental genes related to energy production and carbohydrate metabolism. Genomic metrics including 16S rRNA sequence similarity, average nucleotide identity, and digital DNA-DNA hybridization values were below the cut-off for species delineation, implying that CCB-ST2H9 potentially represents a new species. Genome mining revealed that biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) involved in producing antimicrobial compounds such as holomycin in CCB-ST2H9 could contribute to the antagonistic potential. Furthermore, the EtOAc extract from the culture broth of CCB-ST2H9 exhibited antagonistic activity against Vibrio spp. Intriguingly, clustering based on BGCs profiles grouped P. galatheae, P. halotolerans, P. salinisoli, P. arenosum, and CCB-ST2H9 together in the heatmap by the presence of a large number of BGCs. These BGCs-rich Photobacterium strains represent great potential for bioactive secondary metabolites production and sources for novel compounds.
Keywords: Photobacterium; antagonism; comparative genomics; pan-genome analysis; secondary metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Beijerinck M.W. Le Photobacterium luminosum, bactérie lumineuse de la Mer du Nord. Arch. Neerl. Sci. Exactes Nat. 1889;23:401–427.
-
- Ast J.C., Dunlap P.V. Phylogenetic resolution and habitat specificity of members of the Photobacterium phosphoreum species group. Environ. Microbiol. 2005;7:1641–1654. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

