Acquisition of Streptomycin Resistance by Oxidative Stress Induced by Hydrogen Peroxide in Radiation-Resistant Bacterium Deinococcus geothermalis
- PMID: 36077162
- PMCID: PMC9456066
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23179764
Acquisition of Streptomycin Resistance by Oxidative Stress Induced by Hydrogen Peroxide in Radiation-Resistant Bacterium Deinococcus geothermalis
Abstract
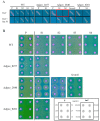
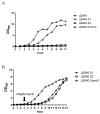
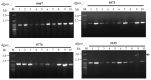
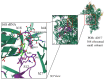
Streptomycin is used primarily to treat bacterial infections, including brucellosis, plague, and tuberculosis. Streptomycin resistance easily develops in numerous bacteria through the inhibition of antibiotic transfer, the production of aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes, or mutations in ribosomal components with clinical doses of streptomycin treatment. (1) Background: A transposable insertion sequence is one of the mutation agents in bacterial genomes under oxidative stress. (2) Methods: In the radiation-resistant bacterium Deinococcus geothermalis subjected to chronic oxidative stress induced by 20 mM hydrogen peroxide, active transposition of an insertion sequence element and several point mutations in three streptomycin resistance (SmR)-related genes (rsmG, rpsL, and mthA) were identified. (3) Results: ISDge6 of the IS5 family integrated into the rsmG gene (dgeo_2335), called SrsmG, encodes a ribosomal guanosine methyltransferase resulting in streptomycin resistance. In the case of dgeo_2840-disrupted mutant strains (S1 and S2), growth inhibition under antibiotic-free conditions was recovered with increased growth yields in the presence of 50 µg/mL streptomycin due to a streptomycin-dependent (SmD) mutation. These mutants have a predicted proline-to-leucine substitution at the 91st residue of ribosomal protein S12 in the decoding center. (4) Conclusions: Our findings show that the active transposition of a unique IS element under oxidative stress conditions conferred antibiotic resistance through the disruption of rsmG. Furthermore, chronic oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide also induced streptomycin resistance caused by point and frameshift mutations of streptomycin-interacting residues such as K43, K88, and P91 in RpsL and four genes for streptomycin resistance.
Keywords: Deinococcus geothermalis; chronic oxidative stress; insertion sequence; phenotypic variation; ribosomal protein S12 (RpsL); streptomycin-dependent (SmD) and -resistant (SmR); transposition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

