Three-Dimensional Envelope and Subunit Interactions of the Plastid-Encoded RNA Polymerase from Sinapis alba
- PMID: 36077319
- PMCID: PMC9456514
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23179922
Three-Dimensional Envelope and Subunit Interactions of the Plastid-Encoded RNA Polymerase from Sinapis alba
Abstract
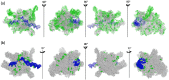
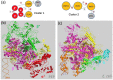
RNA polymerases (RNAPs) are found in all living organisms. In the chloroplasts, the plastid-encoded RNA polymerase (PEP) is a prokaryotic-type multimeric RNAP involved in the selective transcription of the plastid genome. One of its active states requires the assembly of nuclear-encoded PEP-Associated Proteins (PAPs) on the catalytic core, producing a complex of more than 900 kDa, regarded as essential for chloroplast biogenesis. In this study, sequence alignments of the catalytic core subunits across various chloroplasts of the green lineage and prokaryotes combined with structural data show that variations are observed at the surface of the core, whereas internal amino acids associated with the catalytic activity are conserved. A purification procedure compatible with a structural analysis was used to enrich the native PEP from Sinapis alba chloroplasts. A mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomic analysis revealed the core components, the PAPs and additional proteins, such as FLN2 and pTAC18. MS coupled with crosslinking (XL-MS) provided the initial structural information in the form of protein clusters, highlighting the relative position of some subunits with the surfaces of their interactions. Using negative stain electron microscopy, the PEP three-dimensional envelope was calculated. Particles classification shows that the protrusions are very well-conserved, offering a framework for the future positioning of all the PAPs. Overall, the results show that PEP-associated proteins are firmly and specifically associated with the catalytic core, giving to the plastid transcriptional complex a singular structure compared to other RNAPs.
Keywords: PEP associated proteins; Sinapis alba; chloroplast biogenesis; photomorphogenesis; photosynthesis; plastid-encoded RNA polymerase; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

