Homo sapiens May Incorporate Daily Acute Cycles of "Conditioning-Deconditioning" to Maintain Musculoskeletal Integrity: Need to Integrate with Biological Clocks and Circadian Rhythm Mediators
- PMID: 36077345
- PMCID: PMC9456265
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23179949
Homo sapiens May Incorporate Daily Acute Cycles of "Conditioning-Deconditioning" to Maintain Musculoskeletal Integrity: Need to Integrate with Biological Clocks and Circadian Rhythm Mediators
Abstract
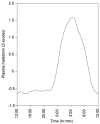
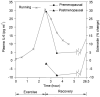
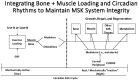
Human evolution required adaptation to the boundary conditions of Earth, including 1 g gravity. The bipedal mobility of Homo sapiens in that gravitational field causes ground reaction force (GRF) loading of their lower extremities, influencing the integrity of the tissues of those extremities. However, humans usually experience such loading during the day and then a period of relative unloading at night. Many studies have indicated that loading of tissues and cells of the musculoskeletal (MSK) system can inhibit their responses to biological mediators such as cytokines and growth factors. Such findings raise the possibility that humans use such cycles of acute conditioning and deconditioning of the cells and tissues of the MSK system to elaborate critical mediators and responsiveness in parallel with these cycles, particularly involving GRF loading. However, humans also experience circadian rhythms with the levels of a number of mediators influenced by day/night cycles, as well as various levels of biological clocks. Thus, if responsiveness to MSK-generated mediators also occurs during the unloaded part of the daily cycle, that response must be integrated with circadian variations as well. Furthermore, it is also possible that responsiveness to circadian rhythm mediators may be regulated by MSK tissue loading. This review will examine evidence for the above scenario and postulate how interactions could be both regulated and studied, and how extension of the acute cycles biased towards deconditioning could lead to loss of tissue integrity.
Keywords: acute conditioning; acute deconditioning; circadian rhythms; connective tissue homeostasis; ground reaction forces; myokines; osteokines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Basti A., Yalcin M., Herms D., Hesse J., Aboumanify O., Li Y., Aretz Z., Garmshausen J., El-Athman R., Hastermann M., et al. Diurnal variations in the expression of core-clock genes correlate with resting muscle properties and predict fluctuations in exercise performance across the day. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2021;7:e000876. doi: 10.1136/bmjsem-2020-000876. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dijk D.J., Shanahan T.L., Duffy J.F., Ronda J.M., Czeisler C.A. Variation of electroencephalographic activity during non-rapid eye movement and rapid eye movement sleep with phase of circadian melatonin rhythm in humans. J. Physiol. 1997;505:851–858. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1997.851ba.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

