Novel Nanotechnology Approaches to Overcome Drug Resistance in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Glypican 3 as a Useful Target for Innovative Therapies
- PMID: 36077433
- PMCID: PMC9456072
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231710038
Novel Nanotechnology Approaches to Overcome Drug Resistance in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Glypican 3 as a Useful Target for Innovative Therapies
Abstract
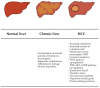
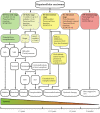
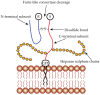
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the second most lethal tumor, with a 5-year survival rate of 18%. Early stage HCC is potentially treatable by therapies with curative intent, whereas chemoembolization/radioembolization and systemic therapies are the only therapeutic options for intermediate or advanced HCC. Drug resistance is a critical obstacle in the treatment of HCC that could be overcome by the use of targeted nanoparticle-based therapies directed towards specific tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) to improve drug delivery. Glypican 3 (GPC3) is a member of the glypican family, heparan sulfate proteoglycans bound to the cell surface via a glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor. The high levels of GPC3 detected in HCC and the absence or very low levels in normal and non-malignant liver make GPC3 a promising TAA candidate for targeted nanoparticle-based therapies. The use of nanoparticles conjugated with anti-GPC3 agents may improve drug delivery, leading to a reduction in severe side effects caused by chemotherapy and increased drug release at the tumor site. In this review, we describe the main clinical features of HCC and the common treatment approaches. We propose the proteoglycan GPC3 as a useful TAA for targeted therapies. Finally, we describe nanotechnology approaches for anti-GPC3 drug delivery systems based on NPs for HCC treatment.
Keywords: drug delivery; glypican 3; hepatocellular carcinoma; nanomedicine; polymeric nanoparticles; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest in this publication.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

