Transcription Factors Runx1 and Runx3 Suppress Keratin Expression in Undifferentiated Keratinocytes
- PMID: 36077435
- PMCID: PMC9456233
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231710039
Transcription Factors Runx1 and Runx3 Suppress Keratin Expression in Undifferentiated Keratinocytes
Abstract
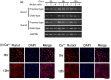
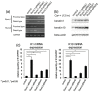
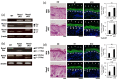
The Runt-related transcription factor (Runx) family has been suggested to play roles in stem cell regulation, tissue development, and oncogenesis in various tissues/organs. In this study, we investigated the possible functions of Runx1 and Runx3 in keratinocyte differentiation. Both Runx1 and Runx3 proteins were detected in primary cultures of mouse keratinocytes. Proteins were localized in the nuclei of undifferentiated keratinocytes but translocated to the cytoplasm of differentiated cells. The siRNA-mediated inhibition of Runx1 and Runx3 expression increased expression of keratin 1 and keratin 10, which are early differentiation markers of keratinocytes. In contrast, overexpression of Runx1 and Runx3 suppressed keratin 1 and keratin 10 expression. Endogenous Runx1 and Runx3 proteins were associated with the promoter sequences of keratin 1 and keratin 10 genes in undifferentiated but not differentiated keratinocytes. In mouse skin, the inhibition of Runx1 and Runx3 expression by keratinocyte-specific gene targeting increased the ratios of keratin 1- and keratin 10-positive cells in the basal layer of the epidermis. On the other hand, inhibition of Runx1 and Runx3 expression did not alter the proliferation capacity of cultured or epidermal keratinocytes. These results suggest that Runx1 and Runx3 likely function to directly inhibit differentiation-induced expression of keratin 1 and keratin 10 genes but are not involved in the regulation of keratinocyte proliferation.
Keywords: differentiation; keratinocyte; proliferation; runt-related transcription factor (Runx).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
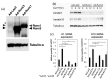

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

