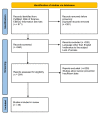
Physical Activity and Cancer Care-A Review
- PMID: 36077690
- PMCID: PMC9454950
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14174154
Physical Activity and Cancer Care-A Review
Abstract
In 2020, 19.3 million new cancer cases were diagnosed, and almost 10 million deaths from cancer were recorded. Cancer patients may experience fatigue, depression, anxiety, reduced quality of life and sleep problems. Cancer treatments cause numerous side effects and have a negative impact on all body systems. Physical activity is important for cancer patients. The aim of this review is to analyse recent studies on the role of physical activity in cancer patients and emphasize its importance. The review included 36 papers published in English between 2017 and 2021. The findings from these studies show that physical activity decreases the severity of side effects of cancer treatment, reduces fatigue, improves quality of life, has a positive impact on mental health and improves aerobic fitness in cancer patients. Moreover, it reduces the risk of cancer recurrence and death. Physical activity is recommended for patients with any type of cancer and at all stages of treatment. The type of physical activity should depend on the condition of the individual patient. It is extremely difficult to determine what type, intensity and duration of physical activity is likely to have the greatest effect.
Keywords: cancer care; physical activity; quality of life; survivors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Carayol M., Ninot G., Senesse P., Bleuse J.P., Gourgou S., Sancho-Garnier H., Jacot W. Short-and long-term impact of adapted physical activity and diet counseling during adjuvant breast cancer therapy: The “APAD1” randomized controlled trial. BMC Cancer. 2019;19:737. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5896-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Campbell K.L., Winters-Stone K., Wiskemann J., May A.M., Schwartz A.L., Courneya K.S., Schmitz K.H. Exercise guidelines for cancer survivors: Consensus statement from international multidisciplinary roundtable. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019;51:2375. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002116. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical