A Novel Artificial Intelligence-Based Approach for Quantitative Assessment of Angiogenesis in the Ex Ovo CAM Model
- PMID: 36077809
- PMCID: PMC9454718
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14174273
A Novel Artificial Intelligence-Based Approach for Quantitative Assessment of Angiogenesis in the Ex Ovo CAM Model
Abstract
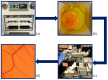
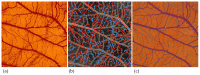
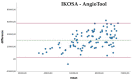
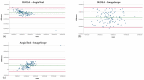
Angiogenesis is a highly regulated process. It promotes tissue regeneration and contributes to tumor growth. Existing therapeutic concepts interfere with different steps of angiogenesis. The quantification of the vasculature is of crucial importance for research on angiogenetic effects. The chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay is widely used in the study of angiogenesis. Ex ovo cultured chick embryos develop an easily accessible, highly vascularised membrane on the surface. Tumor xenografts can be incubated on this membrane enabling studies on cancer angiogenesis and other major hallmarks. However, there is no commonly accepted gold standard for the quantification of the vasculature of the CAM. We compared four widely used measurement techniques to identify the most appropriate one for the quantification of the vascular network of the CAM. The comparison of the different quantification methods suggested that the CAM assay application on the IKOSA platform is the most suitable image analysis application for the vasculature of the CAM. The new CAM application on the IKOSA platform turned out to be a reliable and feasible tool for practical use in angiogenesis research. This novel image analysis software enables a deeper exploration of various aspects of angiogenesis and might support future research on new anti-angiogenic strategies for cancer treatment.
Keywords: angiogenesis; artificial intelligence; chorioallantoic membrane assay; comparison of image analysis methods for angiogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
M.W. and T.E. declare to be employed as computer vision and machine learning engineers by KML vision.
Figures




References
-
- Nowak-Sliwinska P., Alitalo K., Allen E., Anisimov A., Aplin A.C., Auerbach R., Augustin H.G., Bates D.O., van Beijnum J.R., Bender R.H.F., et al. Consensus Guidelines for the Use and Interpretation of Angiogenesis Assays. Angiogenesis. 2018;21:532. doi: 10.1007/s10456-018-9613-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moreno-Jiménez I., Hulsart-Billstrom G., Lanham S.A., Janeczek A.A., Kontouli N., Kanczler J.M., Evans N.D., Oreffo R.O.C. The Chorioallantoic Membrane (CAM) Assay for the Study of Human Bone Regeneration: A Refinement Animal Model for Tissue Engineering. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:32168. doi: 10.1038/srep32168. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

