How Geography and Climate Shaped the Genomic Diversity of Italian Local Cattle and Sheep Breeds
- PMID: 36077919
- PMCID: PMC9454691
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12172198
How Geography and Climate Shaped the Genomic Diversity of Italian Local Cattle and Sheep Breeds
Abstract
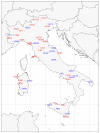
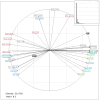
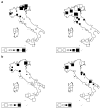
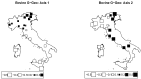
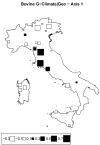
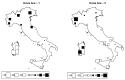
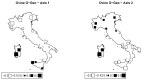
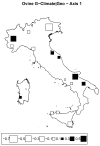
Understanding the relationships among geography, climate, and genetics is increasingly important for animal farming and breeding. In this study, we examine these inter-relationships in the context of local cattle and sheep breeds distributed along the Italian territory. To this aim, we used redundancy analysis on genomic data from previous projects combined with geographical coordinates and corresponding climatic data. The effect of geographic factors (latitude and longitude) was more important in sheep (26.4%) than that in cattle (13.8%). Once geography had been partialled out of analysis, 10.1% of cattle genomic diversity and 13.3% of that of sheep could be ascribed to climatic effects. Stronger geographic effects in sheep can be related to a combination of higher pre-domestication genetic variability together with biological and productive specificities. Climate alone seems to have had less impact on current genetic diversity in both species, even if climate and geography are greatly confounded. Results confirm that both species are the result of complex evolutionary histories triggered by interactions between human needs and environmental conditions.
Keywords: cattle; cilmate; genome; geography; redundancy analysis; sheep.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Felius M., Beerling M.L., Buchanan D.S., Theunissen B., Koolmees P.A., Lenstra J.A. On the history of cattle genetic resources. Diversity. 2014;6:705–750. doi: 10.3390/d6040705. - DOI
-
- Vigne J.D. Early domestication and farming: What should we know or do for a better understanding? Anthropozoologica. 2015;50:123–150. doi: 10.5252/az2015n2a5. - DOI
-
- Fratianni S., Acquaotta F. Landscapes and Landforms of Italy. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2017. The climate of Italy; pp. 29–38.
-
- Ciani E., Ciampolini R., D’Andrea M., Castellana E., Cecchi F., Incoronato C., d’Angelo F., Albenzio M., Pilla F., Matassino D., et al. Analysis of genetic variability within and among Italian sheep breeds reveals population stratification and suggests the presence of a phylogeographic gradient. Small Rumin. Res. 2013;112:21–27. doi: 10.1016/j.smallrumres.2012.12.013. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

