Effect of Treating Eggs with Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) on Growth Variables, Histomorphometry, and Antioxidant Capacity in Red Tilapia (Oreochromis aureus × Oreochromis mossambicus) Larvae
- PMID: 36077939
- PMCID: PMC9454522
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12172219
Effect of Treating Eggs with Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) on Growth Variables, Histomorphometry, and Antioxidant Capacity in Red Tilapia (Oreochromis aureus × Oreochromis mossambicus) Larvae
Abstract
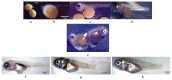
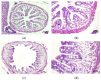
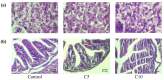
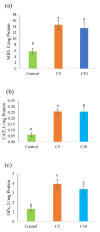
Red tilapia eggs one day post fertilization (dpf) were exposed to coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) at rates of 0, 5, and 10 mg/L for control, treatment 2 (C5), and treatment 3 (C10), respectively, without exchanging water and until the larval mouth-opening stage. Fertilized eggs of red tilapia exposed to different concentrations of CoQ10 were hatched at rates (p > 0.05) between 38 to 54.67%. The yolk-sac diameter at the 2nd day post hatching (dph), ranged from 1.85 to 1.87 mm in depth and 1.63 to 1.88 mm in width and was not altered by the CoQ10 treatments. Similarly, red tilapia survival (p > 0.05) ranged from 22.67 to 32%. On 6 dph, a slight percentage (2.08%) of survived fishes exposed to high CoQ10 dose (C10) exhibited larval deformation in the form of an axial curvature of the spine in the abdominal and caudal region. Larvae displayed a normal structure of the esophagus folds in all fish groups, and larvae in the C5 group displayed the longest folds and widest muscularis layer, followed by fishes in the C10 group and the control. Red tilapia fry on 30 dph treated with CoQ10 possessed higher antioxidant potentials in terms of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) compared to the control. In conclusion, treating Red tilapia fertile eggs with 5 mg/L CoQ10 improves the growth, gut structure, and antioxidant efficiency of the produced larvae.
Keywords: CoQ10; Red tilapia; antioxidants; gut histology; larvae.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zaki M.A.A., Alabssawy A.N., Nour A.E.-A.M., El Basuini M.F., Dawood M.A.O., Alkahtani S., Abdel-Daim M.M. The impact of stocking density and dietary carbon sources on the growth, oxidative status and stress markers of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) reared under biofloc conditions. Aquac. Rep. 2020;16:100282. doi: 10.1016/j.aqrep.2020.100282. - DOI
-
- Cámara-Ruiz M., Santo C.E., Gessner J., Wuertz S. How to improve foraging efficiency for restocking measures of juvenile Baltic sturgeon (Acipenser oxyrinchus) Aquaculture. 2019;502:12–17. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.12.021. - DOI
-
- Hannon C., Officer R.A., Le Dorven J. Review of the technical challenges facing aquaculture of the European abalone Haliotis tuberculata in Ireland. Aquac. Int. 2013;21:243–254. doi: 10.1007/s10499-012-9584-7. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

