Machine Learning and Criminal Justice: A Systematic Review of Advanced Methodology for Recidivism Risk Prediction
- PMID: 36078307
- PMCID: PMC9517748
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph191710594
Machine Learning and Criminal Justice: A Systematic Review of Advanced Methodology for Recidivism Risk Prediction
Abstract
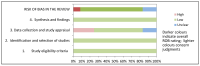
Recent evolution in the field of data science has revealed the potential utility of machine learning (ML) applied to criminal justice. Hence, the literature focused on finding better techniques to predict criminal recidivism risk is rapidly flourishing. However, it is difficult to make a state of the art for the application of ML in recidivism prediction. In this systematic review, out of 79 studies from Scopus and PubMed online databases we selected, 12 studies that guarantee the replicability of the models across different datasets and their applicability to recidivism prediction. The different datasets and ML techniques used in each of the 12 studies have been compared using the two selected metrics. This study shows how each method applied achieves good performance, with an average score of 0.81 for ACC and 0.74 for AUC. This systematic review highlights key points that could allow criminal justice professionals to routinely exploit predictions of recidivism risk based on ML techniques. These include the presence of performance metrics, the use of transparent algorithms or explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) techniques, as well as the high quality of input data.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; crime prediction; explainable artificial intelligence; machine learning; recidivism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Newton A., May X., Eames S., Ahmad M. Economic and Social Costs of Reoffending Analytical Report. [(accessed on 18 June 2022)]; Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploa....
-
- Waller M.A., Fawcett S.E. Data science, predictive analytics, and big data: A revolution that will transform supply chain design and management. J. Bus. Logist. 2013;34:77–84. doi: 10.1111/jbl.12010. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources