Ergonomic Improvements to Agricultural Harvest Baskets to Reduce the Risk of Musculoskeletal Disorders among Farmers
- PMID: 36078384
- PMCID: PMC9518395
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph191710669
Ergonomic Improvements to Agricultural Harvest Baskets to Reduce the Risk of Musculoskeletal Disorders among Farmers
Abstract
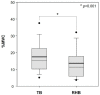
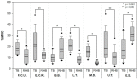
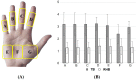
Typical harvesting baskets (TB) are used in various agricultural workplaces; however, no study to date has reported their effect on the musculoskeletal system. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the effects of a novel basket with attached rotational handles (RHB) to help alleviate the work-related physical burden of farmers. We analyzed the surface electromyograms (EMGs) of seven muscles, evaluated the subjective discomfort levels and locally perceived discomfort (LPD) scores to investigate the discomfort in the whole body and seven hand muscles, respectively. The EMGs showed that muscle activity decreased in five muscles (flexor carpi ulnaris, extensor carpi radialis, lateral triceps, middle deltoid, and upper trapezius) and increased in two (biceps brachii and erector spinae) when the RHB was used (p < 0.05). The subjective discomfort score for the RHB decreased compared to that for TB (p < 0.001). The LPD scores also decreased, and the RHB and TB scores ranged from 1.25-1.40 and 3.1-3.25, respectively. The use of the RHB may prevent wrist bending, and reduce the activity of certain muscles while increasing the activity of other muscles. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct training and to evaluate the working posture while considering the affected muscles.
Keywords: electromyography; ergonomics; farmer; harvesting basket; musculoskeletal burden.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Guidelines for Working Heights of the Lower-Limb Exoskeleton (CEX) Based on Ergonomic Evaluations.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 May 13;18(10):5199. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18105199. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34068352 Free PMC article.
-
Design and ergonomic evaluation of a new adapted endoscope holder to reduce muscle pressure and discomfort during endoscopy.Work. 2023;76(1):403-410. doi: 10.3233/WOR-220185. Work. 2023. PMID: 36776095
-
Ergonomics investigation for orientation of the handles of wood routers.Int J Occup Saf Ergon. 2018 Dec;24(4):592-604. doi: 10.1080/10803548.2017.1373479. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Int J Occup Saf Ergon. 2018. PMID: 28868989
-
Effects of industrial back-support exoskeletons on body loading and user experience: an updated systematic review.Ergonomics. 2021 Jun;64(6):685-711. doi: 10.1080/00140139.2020.1870162. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Ergonomics. 2021. PMID: 33369518
-
Ergonomic interventions for preventing work-related musculoskeletal disorders of the upper limb and neck among office workers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 23;10(10):CD008570. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008570.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30350850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) Musculoskeletal Disorders and Workplace Factors. Publication number 97–141. [(accessed on 25 July 2022)];1997 Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/97-141/pdfs/97-141.pdf?id=10.26616/NIOSHP....
-
- Afonso M., Gabriel A.T., Godina R. Proposal of an innovative ergonomic SMED model in an automotive steel springs industrial unit. Adv. Ind. Manuf. Eng. 2022;4:100075. doi: 10.1016/j.aime.2022.100075. - DOI
-
- Pimparel A., Madaleno S., Ollay C., Gabriel A.T. How Ergonomic Evaluations Influence the Risk of Musculoskeletal Disorders in the Industrial Context? A Brief Literature Review. Stud. Syst. Decis. Control. 2022;406:399–409. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-89617-1_36. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

