The Effect of UV Treatment on Surface Contact Angle, Fibroblast Cytotoxicity, and Proliferation with Two Types of Zirconia-Based Ceramics
- PMID: 36078826
- PMCID: PMC9518570
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph191711113
The Effect of UV Treatment on Surface Contact Angle, Fibroblast Cytotoxicity, and Proliferation with Two Types of Zirconia-Based Ceramics
Abstract
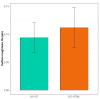
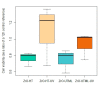
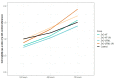
UV photofunctionalization of Zirconia-based materials for abutment fabrication is a promising approach that might influence the formation of a sound peri-implant seal, thus promoting long-term soft and hard tissue implant integration. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of UV treatment of test specimens made by two different ZnO2-based ceramic materials on the hydrophilicity, cell cytotoxicity, and proliferation of human gingival fibroblasts (HGFs). Two Zirconia-based materials, high-translucent and ultra-translucent multi-layered Zirconia (Katana, Kuraray Noritake, Japan), were used to prepare a total of 40 specimens distributed in two equally sized groups based on the material (n = 20). The same surface finishing protocol was applied for all specimens, as suggested by the manufacturer. Half the specimens from each group were treated with UV-C light for 48 h. Water contact angle (WCA), fibroblast cytotoxicity, and proliferation were investigated. The WCA values for the high-translucent Zirconia ranged from 69.9° ± 6.4° to 73.7° ± 13.9° for the treated/non-treated specimens and from 79.5° ± 12.8° to 83.4° ± 11.4° for the ultra-translucent multi-layered Zirconia, respectively. However, the difference was insignificant (F(16) = 3.50, p = 0.292). No significant difference was observed for the fibroblast cytotoxicity test. The results for proliferation revealed a significant difference, which was material-dependent (F(8) = 9.58, p = 0.005). We found that UV surface photofunctionalization of ZrO2-based materials alters the human gingival fibroblast cell viability, which might produce favourable results for cell proliferation.
Keywords: UV photofunctionalization; fibroblast proliferation; surface roughness; water contact angle; zirconia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ultraviolet light-treated zirconia with different roughness affects function of human gingival fibroblasts in vitro: the potential surface modification developed from implant to abutment.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015 Jan;103(1):116-24. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33183. Epub 2014 Apr 28. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015. PMID: 24771524
-
Effect of Microporous Surface Zirconia on Mechanical Properties and Biological Behavior of Human Gingival Fibroblasts.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2025 Mar;113(3):e35547. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.35547. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2025. PMID: 39969110
-
Evaluation of the biological behaviour of various dental implant abutment materials on attachment and viability of human gingival fibroblasts.Dent Mater. 2019 Jul;35(7):1053-1063. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2019.04.010. Epub 2019 May 3. Dent Mater. 2019. PMID: 31060818
-
[Translucent zirconia ceramics for fabrication monolithic restorations: review. Part 2].Stomatologiia (Mosk). 2020;99(6):101-106. doi: 10.17116/stomat202099061101. Stomatologiia (Mosk). 2020. PMID: 33267553 Review. Russian.
-
Human gingival fibroblast proliferation on materials used for dental implant abutments: a systematic review.Int J Prosthodont. 2021 November/December;34(6):811–828. doi: 10.11607/ijp.7388. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Int J Prosthodont. 2021. PMID: 33616578
Cited by
-
Current classification of zirconia in dentistry: an updated review.PeerJ. 2023 Jul 14;11:e15669. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15669. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37465158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contour Analysis of Three-Dimensional Peri-Implant Mucosal Model as an Endpoint Analysis of Photofunctionalization Effects on Implant Abutment Materials.Materials (Basel). 2023 Aug 9;16(16):5529. doi: 10.3390/ma16165529. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37629819 Free PMC article.
-
Implant Surface Decontamination Methods That Can Impact Implant Wettability.Materials (Basel). 2024 Dec 20;17(24):6249. doi: 10.3390/ma17246249. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39769848 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al Rezk F., Trimpou G., Lauer H.-C., Weigl P., Krockow N. Response of Soft Tissue to Different Abutment Materials with Different Surface Topographies: A Review of the Literature. Gen. Dent. 2018;66:18–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

