The Genomic Environment of BRAF Mutated and BRAF/ PIK3CA Double Mutated Colorectal Cancers
- PMID: 36079062
- PMCID: PMC9456575
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11175132
The Genomic Environment of BRAF Mutated and BRAF/ PIK3CA Double Mutated Colorectal Cancers
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer represents the most prevalent gastrointestinal malignancy. Prognosis of metastatic disease has improved in recent years with the introduction of effective systemic therapies, but mean survival remains in the range of two to three years. Targeted therapies based on specific molecular alterations in sub-sets of colorectal cancers have the potential of contributing to therapeutic progress. BRAF and PIK3CA are oncogenic kinases commonly mutated in colorectal cancers and can be targeted through small molecule kinase inhibitors.
Methods: Clinical and genomic data from two extensive series of colorectal cancers were interrogated to define the molecular characteristics of cancers with BRAF mutations with and without concomitant mutations in PIK3CA.
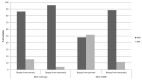
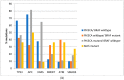
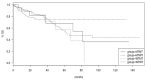
Results: Colorectal cancers that are BRAF and PIK3CA double mutants represent a small minority of about 5% of colorectal cancers in the two examined series of mostly localized disease. They also represent about one third of all BRAF mutated colorectal cancers. Most mutations in BRAF are classic V600E mutations. A high prevalence of MSI and CIMP is observed in BRAF mutated colorectal cancers with or without PIK3CA mutations. Mutations in tumor suppressors FBXW7 and ATM display a higher prevalence in BRAF mutated cancers. The prognosis of BRAF mutated colorectal cancers with or without PIK3CA mutations is not significantly different than counterparts with wild type BRAF. This contrasts with the known adverse prognostic effect of BRAF in metastatic disease and relates to the different prevalence of MSI in mutant BRAF localized versus metastatic colorectal cancers.
Conclusions: BRAF mutations are the defining molecular alterations in double mutant BRAF and PIK3CA colorectal cancers as determined by increased MSI and CIMP in BRAF subsets with and without PIK3CA mutations. Moreover, BRAF mutated cancers with and without PIK3CA mutations are characterized by the absence of KRAS mutations and a lower prevalence of APC mutations than BRAF wild type counterparts. Mismatch-repair-associated gene mutations display higher frequencies in BRAF mutated colorectal cancers. Despite the absence of prognosis implications of BRAF mutations in the studied cohorts of mostly localized cancers, such mutations could be prognostic in certain subsets. The presence of mutations in other genes, such as ATM and high MSI status present opportunities for combination therapies.
Keywords: gastrointestinal cancers; genomics; kinase; molecular alterations; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

