Systematic Review of Risk Factors Assessed in Predictive Scoring Tools for Drug-Related Problems in Inpatients
- PMID: 36079114
- PMCID: PMC9457151
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11175185
Systematic Review of Risk Factors Assessed in Predictive Scoring Tools for Drug-Related Problems in Inpatients
Abstract
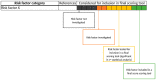
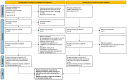
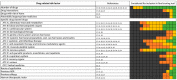
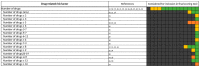
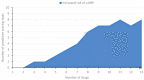
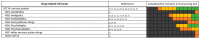
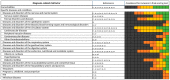
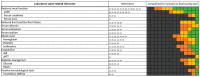
Drug-related problems (DRP, defined as adverse drug events/reactions and medication errors) are a common threat for patient safety. With the aim to aid improved allocation of specialist resources and to improve detection and prevention of DRP, numerous predictive scoring tools have been proposed. The external validation and evidence for the transferability of these tools still faces limitations. However, the proposed scoring tools include partly overlapping sets of similar factors, which may allow a new approach to estimate the external usability and validity of individual risk factors. Therefore, we conducted this systematic review and analysis. We identified 14 key studies that assessed 844 candidate risk factors for inclusion into predictive scoring tools. After consolidation to account for overlapping terminology and variable definitions, we assessed each risk factor in the number of studies it was assessed, and, if it was found to be a significant predictor of DRP, whether it was included in a final scoring tool. The latter included intake of ≥ 8 drugs, drugs of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) class N, ≥1 comorbidity, an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <30 mL/min and age ≥60 years. The methodological approach and the individual risk factors presented in this review may provide a new starting point for improved risk assessment.
Keywords: adverse drug events; adverse drug reactions; clinical pharmacology; clinical pharmacy; drug-related problems; medication errors; predictive scoring tool; risk assessment; risk factors; risk score.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, the data collection, the analyses, the interpretation of data, the writing of the manuscript and the decision to publish the results.
Figures

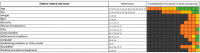
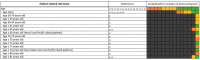


References
-
- Meier F., Maas R., Sonst A., Patapovas A., Müller F., Plank-Kiegele B., Pfistermeister B., Schöffski O., Bürkle T., Dormann H. Adverse drug events in patients admitted to an emergency department: An analysis of direct costs. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2015;24:176–186. doi: 10.1002/pds.3663. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

