The Effects of Statin Treatment on Serum Ferritin Levels: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36079181
- PMCID: PMC9457426
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11175251
The Effects of Statin Treatment on Serum Ferritin Levels: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Statins are the most widely used drugs for decreasing elevated serum LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C) and thus for the prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), but they have also some pleiotropic effects, including anti-inflammatory properties. Atherosclerosis is a low-grade inflammatory disease, and elevated ferritin is considered to be one of the markers of inflammation. Since the results of studies on the effects of statins on serum ferritin levels are conflicting, this meta-analysis was performed.
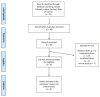
Methods: A literature search was performed using major electronic databases (MEDLINE/PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and ISI Web of Science) from inception up to 5 March 2022 to find studies evaluating the effect of different statins on serum ferritin levels. The effect size was determined using weighted mean differences (WMDs) and the corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
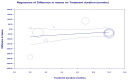
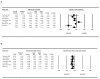
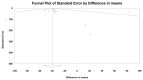
Results: The meta-analysis of nine studies (1611 patients) analyzing the effects of statins on serum ferritin levels that were included showed a significant decrease in circulating ferritin levels caused by statins. The results did not suggest any significant association between the changes in concentrations of serum ferritin and the duration of treatment with statins.
Conclusions: Statin therapy decreases the circulating concentrations of ferritin, which might be beneficial for the prevention and/or progression of ASCVD. This effect might be explained by the anti-inflammatory effects and maybe some other pleiotropic effects of statins and not by their lipid-lowering effects.
Keywords: acute-phase response; cardiovascular diseases; inflammation; iron; lipid-lowering therapy; statins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Effects of Statin Dose, Lipophilicity, and Combination of Statins plus Ezetimibe on Circulating Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Levels: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Sep 4;2021:9661752. doi: 10.1155/2021/9661752. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34526854 Free PMC article.
-
Ezetimibe for the prevention of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality events.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 19;11(11):CD012502. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012502.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30480766 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Statins on the Blood Lipid Profile in Patients with Different Cardiovascular Diseases: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.Curr Med Chem. 2023;30(32):3702-3724. doi: 10.2174/0929867330666221129094921. Curr Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36453499
-
Adding ezetimibe to statin therapy: latest evidence and clinical implications.Drugs Context. 2018 Jul 9;7:212534. doi: 10.7573/dic.212534. eCollection 2018. Drugs Context. 2018. PMID: 30023003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Statin Therapy on Arterial Wall Inflammation Based on 18F-FDG PET/CT: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Interventional Studies.J Clin Med. 2019 Jan 18;8(1):118. doi: 10.3390/jcm8010118. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 30669380 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Possible link between statin and iron deficiency anemia: A South Korean nationwide population-based cohort study.Sci Adv. 2023 Oct 27;9(43):eadg6194. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg6194. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37889968 Free PMC article.
-
Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Decreases the Expression of Adenosine A2A Receptor and Lipid Rafts-Protein Flotillin-1: Insights on Cardiovascular Risk of Hypercholesterolemia.Cells. 2024 Mar 11;13(6):488. doi: 10.3390/cells13060488. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38534331 Free PMC article.
-
Simvastatin-Mediated Nrf2 Activation Induces Fetal Hemoglobin and Antioxidant Enzyme Expression to Ameliorate the Phenotype of Sickle Cell Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Mar 11;13(3):337. doi: 10.3390/antiox13030337. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539870 Free PMC article.
-
Rosuvastatin accelerates the healing process of partial-thickness burn wounds in rats by reducing TNF-α levels.Arch Med Sci Atheroscler Dis. 2024 Dec 31;9:e226-e240. doi: 10.5114/amsad/196825. eCollection 2024. Arch Med Sci Atheroscler Dis. 2024. PMID: 40007987 Free PMC article.
-
Association between soluble transferrin receptor and systolic hypertension in adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2007-2010 and 2015-2018).Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Nov 4;9:1029714. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1029714. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36407469 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mk J., Ridker P.M. Anti-inflammatory effects of statins: Clinical evidence and basic mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005;4:977–987. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

