Reduced Graphene Oxide Modulates the FAK-Dependent Signaling Pathway in Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells In Vitro
- PMID: 36079225
- PMCID: PMC9457042
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15175843
Reduced Graphene Oxide Modulates the FAK-Dependent Signaling Pathway in Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells In Vitro
Abstract
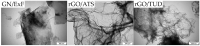
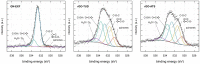
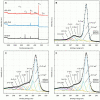
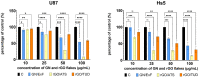
Aggressive invasiveness is a common feature of malignant gliomas, despite their high level of tumor heterogeneity and possible diverse cell origins. Therefore, it is important to explore new therapeutic methods. In this study, we evaluated and compared the effects of graphene (GN) and reduced graphene oxides (rGOs) on a highly invasive and neoplastic cell line, U87. The surface functional groups of the GN and rGO flakes were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The antitumor activity of these flakes was obtained by using the neutral red assay and their anti-migratory activity was determined using the wound healing assay. Further, we investigated the mRNA and protein expression levels of important cell adhesion molecules involved in migration and invasiveness. The rGO flakes, particularly rGO/ATS and rGO/TUD, were found highly toxic. The migration potential of both U87 and Hs5 cells decreased, especially after rGO/TUD treatment. A post-treatment decrease in mobility and FAK expression was observed in U87 cells treated with rGO/ATS and rGO/TUD flakes. The rGO/TUD treatment also reduced β-catenin expression in U87 cells. Our results suggest that rGO flakes reduce the migration and invasiveness of U87 tumor cells and can, thus, be used as potential antitumor agents.
Keywords: FAK; U87 cell line; cell membrane receptors; cell mobility; glioblastoma; graphene; invasiveness; migration; reduced graphene oxide; β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Reduced Graphene Oxides Modulate the Expression of Cell Receptors and Voltage-Dependent Ion Channel Genes of Glioblastoma Multiforme.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 6;22(2):515. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020515. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33419226 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Reduced Graphene Oxides on Apoptosis and Cell Cycle of Glioblastoma Multiforme.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 7;19(12):3939. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123939. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30544611 Free PMC article.
-
Graphene Functionalized with Arginine Decreases the Development of Glioblastoma Multiforme Tumor in a Gene-Dependent Manner.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Oct 23;16(10):25214-33. doi: 10.3390/ijms161025214. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26512645 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo effects of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide on glioblastoma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2015 Feb 25;10:1585-96. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S77591. eCollection 2015. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015. PMID: 25759581 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress-mediated antibacterial activity of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:5901-14. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S37397. Epub 2012 Nov 30. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 23226696 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Potential Role of Carbon Nanomaterials in the Treatment of Malignant Brain Gliomas.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 30;15(9):2575. doi: 10.3390/cancers15092575. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37174040 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stupp R., Mason W.P., van den Bent M.J., Weller M., Fisher B., Taphoorn M.J., Belanger K., Brandes A.A., Marosi C., Bogdahn U., et al. European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups, National Cancer Institute of Canada W. Wu et al. Pharmacol. Res. 2021;171:10578017.
-
- Verhaak R.G., Hoadley K.A., Purdom E., Wang V., Qi Y., Wilkerson M.D., Miller C.R., Ding L., Golub T., Mesirov J.P., et al. Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell. 2010;17:98–110. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.12.020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

