Conductive Inks Based on Melamine Intercalated Graphene Nanosheets for Inkjet Printed Flexible Electronics
- PMID: 36079974
- PMCID: PMC9457697
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12172936
Conductive Inks Based on Melamine Intercalated Graphene Nanosheets for Inkjet Printed Flexible Electronics
Abstract
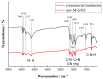
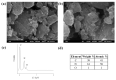
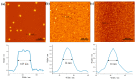
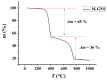
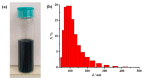
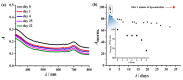
With the growing number of flexible electronics applications, environmentally benign ways of mass-producing graphene electronics are sought. In this study, we present a scalable mechanochemical route for the exfoliation of graphite in a planetary ball mill with melamine to form melamine-intercalated graphene nanosheets (M-GNS). M-GNS morphology was evaluated, revealing small particles, down to 14 nm in diameter and 0.4 nm thick. The M-GNS were used as a functional material in the formulation of an inkjet-printable conductive ink, based on green solvents: water, ethanol, and ethylene glycol. The ink satisfied restrictions regarding stability and nanoparticle size; in addition, it was successfully inkjet printed on plastic sheets. Thermal and photonic post-print processing were evaluated as a means of reducing the electrical resistance of the printed features. Minimal sheet resistance values (5 kΩ/sq for 10 printed layers and 626 Ω/sq for 20 printed layers) were obtained on polyimide sheets, after thermal annealing for 1 h at 400 °C and a subsequent single intense pulsed light flash. Lastly, a proof-of-concept simple flexible printed circuit consisting of a battery-powered LED was realized. The demonstrated approach presents an environmentally friendly alternative to mass-producing graphene-based printed flexible electronics.
Keywords: conductive ink; graphene nanosheets; inkjet printing; mechanochemistry; printed electronics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Raut N.C., Al-Shamery K. Inkjet printing metals on flexible materials for plastic and paper electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2018;6:1618–1641. doi: 10.1039/C7TC04804A. - DOI
-
- Nayak L., Mohanty S., Nayak S.K., Ramadoss A. A review on inkjet printing of nanoparticle inks for flexible electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2019;7:8771–8795. doi: 10.1039/C9TC01630A. - DOI
-
- Huang L., Huang Y., Liang J., Wan X., Chen Y. Graphene-based conducting inks for direct inkjet printing of flexible conductive patterns and their applications in electric circuits and chemical sensors. Nano Res. 2011;4:675–684. doi: 10.1007/s12274-011-0123-z. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

