Lipid-Based Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery Systems in Breast Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 36079985
- PMCID: PMC9458017
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12172948
Lipid-Based Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery Systems in Breast Cancer Therapy
Abstract
Globally, breast cancer is one of the most prevalent diseases, inducing critical intimidation to human health. Lipid-based nanomaterials have been successfully demonstrated as drug carriers for breast cancer treatment. To date, the development of a better drug delivery system based on lipid nanomaterials is still urgent to make the treatment and diagnosis easily accessible to breast cancer patients. In a drug delivery system, lipid nanomaterials have revealed distinctive features, including high biocompatibility and efficient drug delivery. Specifically, a targeted drug delivery system based on lipid nanomaterials has inherited the advantage of optimum dosage and low side effects. In this review, insights on currently used potential lipid-based nanomaterials are collected and introduced. The review sheds light on conjugation, targeting, diagnosis, treatment, and clinical significance of lipid-based nanomaterials to treat breast cancer. Furthermore, a brighter side of lipid-based nanomaterials as future potential drug delivery systems for breast cancer therapy is discussed.
Keywords: breast cancer; conjugation; drug delivery system; efficacy; exosomes; liposomes; micelles; safety; targeting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
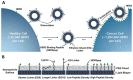

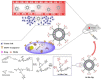
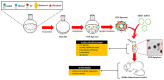

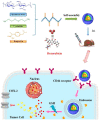

References
-
- Chang T.-W., Ko H., Huang W.-S., Chiu Y.-C., Yang L.-X., Chia Z.-C., Chin Y.-C., Chen Y.-J., Tsai Y.-T., Hsu C.-W., et al. Tannic acid-induced interfacial ligand-to-metal charge transfer and the phase transformation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles for the photothermal bacteria destruction. Chem. Eng. J. 2022;428:131237. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131237. - DOI
-
- Hsu I.L., Yeh F.H., Chin Y.-C., Cheung C.I., Chia Z.C., Yang L.-X., Chen Y.-J., Cheng T.-Y., Wu S.-P., Tsai P.-J., et al. Multiplex antibacterial processes and risk in resistant phenotype by high oxidation-state nanoparticles: New killing process and mechanism investigations. Chem. Eng. J. 2021;409:128266. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.128266. - DOI
-
- Yang Y.-T., Hsu I.L., Cheng T.-Y., Wu W.-J., Lee C.-W., Li T.-J., Cheung C.I., Chin Y.-C., Chen H.-C., Chiu Y.-C., et al. Off-resonance SERS nanoprobe-targeted screen of biomarkers for antigens recognition of bladder normal and aggressive cancer cells. Anal. Chem. 2019;91:8213–8220. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00775. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mutalik C., Krisnawati D.I., Patil S.B., Khafid M., Atmojo D.S., Santoso P., Lu S.-C., Wang D.-Y., Kuo T.-R. Phase-dependent MoS2 nanoflowers for light-driven antibacterial application. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021;9:7904–7912. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c01868. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

