Direct Identification of Urinary Tract Pathogens by MALDI-TOF/TOF Analysis and De Novo Peptide Sequencing
- PMID: 36080229
- PMCID: PMC9457756
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27175461
Direct Identification of Urinary Tract Pathogens by MALDI-TOF/TOF Analysis and De Novo Peptide Sequencing
Abstract
For mass spectrometry-based diagnostics of microorganisms, matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) is currently routinely used to identify urinary tract pathogens. However, it requires a lengthy culture step for accurate pathogen identification, and is limited by a relatively small number of available species in peptide spectral libraries (≤3329). Here, we propose a method for pathogen identification that overcomes the above limitations, and utilizes the MALDI-TOF/TOF MS instrument. Tandem mass spectra of the analyzed peptides were obtained by chemically activated fragmentation, which allowed mass spectrometry analysis in negative and positive ion modes. Peptide sequences were elucidated de novo, and aligned with the non-redundant National Center for Biotechnology Information Reference Sequence Database (NCBInr). For data analysis, we developed a custom program package that predicted peptide sequences from the negative and positive MS/MS spectra. The main advantage of this method over a conventional MALDI-TOF MS peptide analysis is identification in less than 24 h without a cultivation step. Compared to the limited identification with peptide spectra libraries, the NCBI database derived from genome sequencing currently contains 20,917 bacterial species, and is constantly expanding. This paper presents an accurate method that is used to identify pathogens grown on agar plates, and those isolated directly from urine samples, with high accuracy.
Keywords: de novo peptide sequencing; peptide identification software; tandem mass spectrometry; uropathogenic infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

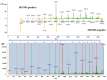
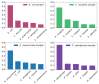
References
-
- Zauli D.A.G. PCR and Infectious Diseases. Synth. Biol.-New Interdiscip. Sci. 2019:137–147. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.85630. - DOI
-
- Church D.L., Cerutti L., Gürtler A., Griener T., Zelazny A., Emler S. Performance and Application of 16S RRNA Gene Cycle Sequencing for Routine Identification of Bacteria in the Clinical Microbiology Laboratory. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020;33:e00053-19. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00053-19. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

