Dissipation, Processing Factors and Dietary Risk Assessment for Flupyradifurone Residues in Ginseng
- PMID: 36080241
- PMCID: PMC9457792
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27175473
Dissipation, Processing Factors and Dietary Risk Assessment for Flupyradifurone Residues in Ginseng
Abstract
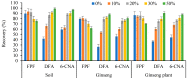
The massive use of pesticides has brought great risks to food and environmental safety. It is necessary to develop reliable analytical methods and evaluate risks through monitoring studies. Here, a method was used for the simultaneous determination of flupyradifurone (FPF) and its two metabolites in fresh ginseng, dried ginseng, ginseng plants, and soil. The method exhibited good accuracy (recoveries of 72.8-97.5%) and precision (relative standard deviations of 1.1-8.5%). The field experiments demonstrated that FPF had half-lives of 4.5-7.9 d and 10.0-16.9 d in ginseng plants and soil, respectively. The concentrations of total terminal residues in soil, ginseng plants, dried ginseng, and ginseng were less than 0.516, 2.623, 2.363, and 0.641 mg/kg, respectively. Based on these results, the soil environmental risk assessment shows that the environmental risk of FPF to soil organisms is acceptable. The processing factors for FPF residues in ginseng were 3.82-4.59, indicating that the concentration of residues increased in ginseng after drying. A dietary risk assessment showed that the risk of FPF residues from long-term and short-term dietary exposures to global consumers were 0.1-0.4% and 12.07-13.16%, respectively, indicating that the application of FPF to ginseng at the recommended dose does not pose a significant risk to consumers.
Keywords: analytical method; flupyradifurone; ginseng; mass spectrometry; pesticide residue analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dissipation and residue analysis of novel nematicide trifluorocide in ginseng and soil using modified QuEChERS method coupled with HPLC-MS/MS.J Environ Sci Health B. 2021;56(12):1042-1050. doi: 10.1080/03601234.2021.2007016. Epub 2021 Nov 30. J Environ Sci Health B. 2021. PMID: 34846269
-
Dissipation and Risk Assessment of Propaquizafop in Ginseng under Field Conditions.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Mar 27;72(12):6613-6624. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c07832. Epub 2024 Mar 19. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38501445
-
Dissipation and residues determination of propamocarb in ginseng and soil by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry.Environ Monit Assess. 2014 Sep;186(9):5327-36. doi: 10.1007/s10661-014-3781-y. Epub 2014 May 4. Environ Monit Assess. 2014. PMID: 24791956
-
Dissipation, residues, and safety evaluation of trifloxystrobin and tebuconazole on ginseng and soil.Environ Monit Assess. 2015 Jun;187(6):344. doi: 10.1007/s10661-015-4591-6. Epub 2015 May 12. Environ Monit Assess. 2015. PMID: 25963765
-
Determination, residue analysis, dietary risk assessment, and processing of flupyradifurone and its metabolites in pepper under field conditions using LC-MS/MS.Biomed Chromatogr. 2022 Apr;36(4):e5312. doi: 10.1002/bmc.5312. Epub 2022 Jan 22. Biomed Chromatogr. 2022. PMID: 34981517
Cited by
-
Dissipation study of ten insecticides in apples under field conditions.J Sci Food Agric. 2025 Sep;105(12):6603-6614. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.14370. Epub 2025 May 12. J Sci Food Agric. 2025. PMID: 40353567 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous Determination of 108 Pesticide Residues in Three Traditional Chinese Medicines Using a Modified QuEChERS Mixed Sample Preparation Method and HPLC-MS/MS.Molecules. 2022 Nov 7;27(21):7636. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217636. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yanan L., Dongyue Z., Min L., Chenyun H., Yong L., Wanlong D. Investigation of Pests and Diseases Occurrence and Pesticides Application in Main Producing Areas of Panax ginseng. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2014;30:294–298.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

