Small Molecule Inhibitors for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Advances and Challenges
- PMID: 36080304
- PMCID: PMC9457820
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27175537
Small Molecule Inhibitors for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Advances and Challenges
Abstract
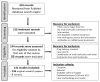
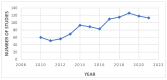
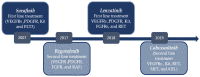
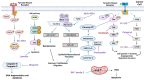
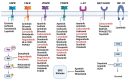
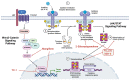
According to data provided by World Health Organization, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common cause of deaths due to cancer worldwide. Tremendous progress has been achieved over the last 10 years developing novel agents for HCC treatment, including small-molecule kinase inhibitors. Several small molecule inhibitors currently form the core of HCC treatment due to their versatility since they would be more easily absorbed and have higher oral bioavailability, thus easier to formulate and administer to patients. In addition, they can be altered structurally to have greater volumes of distribution, allowing them to block extravascular molecular targets and to accumulate in a high concentration in the tumor microenvironment. Moreover, they can be designed to have shortened half-lives to control for immune-related adverse events. Most importantly, they would spare patients, healthcare institutions, and society as a whole from the burden of high drug costs. The present review provides an overview of the pharmaceutical compounds that are licensed for HCC treatment and other emerging compounds that are still investigated in preclinical and clinical trials. These molecules are targeting different molecular targets and pathways that are proven to be involved in the pathogenesis of the disease.
Keywords: HCC pathways inhibitors; growth factor receptors inhibitors; hepatocellular carcinoma; molecular targets; small molecule inhibitors; small molecules as immunomodulators; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Milestones in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2021 Jan;157:103179. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2020.103179. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2021. PMID: 33302158
-
Targeting Jak/Stat pathway as a therapeutic strategy against SP/CD44+ tumorigenic cells in Akt/β-catenin-driven hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2020 Jan;72(1):104-118. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.08.035. Epub 2019 Sep 18. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31541681
-
Strategies to Improve the Antitumor Effect of Immunotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 26;12:783236. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.783236. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34899747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolving molecular mechanism-based strategies for control of hepatocellular carcinoma.Curr Med Chem. 2011;18(28):4375-88. doi: 10.2174/092986711797200462. Curr Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21861817 Review.
-
Targeting receptor tyrosine kinase pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011 Jul;11(6):560-75. doi: 10.2174/187152011796011055. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21554207 Review.
Cited by
-
STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Health and Disease.MedComm (2020). 2025 Mar 30;6(4):e70152. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70152. eCollection 2025 Apr. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40166646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small-molecule-based targeted therapy in liver cancer.Mol Ther. 2024 Oct 2;32(10):3260-3287. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.08.001. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 39113358 Review.
-
Virtual Screening and Biological Evaluation of Potential PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors as Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Agents.ACS Omega. 2023 Sep 3;8(37):33242-33254. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00279. eCollection 2023 Sep 19. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37744828 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell mitophagy patterns within the tumor microenvironment modulate intercellular communication, impacting the progression and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 6;15:1448878. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1448878. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39835122 Free PMC article.
-
Sorafenib Alleviates Inflammatory Signaling of Tumor Microenvironment in Precancerous Lung Injuries.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Feb 1;16(2):221. doi: 10.3390/ph16020221. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37259369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elghazaly H., Gaballah A., Eldin N.B. Clinic-Pathological Pattern of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (Hcc) in Egypt. Ann. Oncol. 2018;29:v5–v6. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy151.018. - DOI
-
- Savitha G., Vishnupriya V., Krishnamohan S. Hepatocellular Carcinoma—A Review. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017;9:1276–1280. doi: 10.15586/jrenhep.v4i2.84. - DOI
-
- Systemic Treatment for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma—UpToDate. [(accessed on 23 November 2021)]. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/systemic-treatment-for-advanced-hepato....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

