Therapeutic Potential of Small Molecules Targeting Oxidative Stress in the Treatment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 36080309
- PMCID: PMC9458015
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27175542
Therapeutic Potential of Small Molecules Targeting Oxidative Stress in the Treatment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
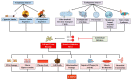
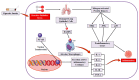
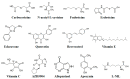
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is an increasing and major global health problem. COPD is also the third leading cause of death worldwide. Oxidative stress (OS) takes place when various reactive species and free radicals swamp the availability of antioxidants. Reactive nitrogen species, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and their counterpart antioxidants are important for host defense and physiological signaling pathways, and the development and progression of inflammation. During the disturbance of their normal steady states, imbalances between antioxidants and oxidants might induce pathological mechanisms that can further result in many non-respiratory and respiratory diseases including COPD. ROS might be either endogenously produced in response to various infectious pathogens including fungi, viruses, or bacteria, or exogenously generated from several inhaled particulate or gaseous agents including some occupational dust, cigarette smoke (CS), and air pollutants. Therefore, targeting systemic and local OS with therapeutic agents such as small molecules that can increase endogenous antioxidants or regulate the redox/antioxidants system can be an effective approach in treating COPD. Various thiol-based antioxidants including fudosteine, erdosteine, carbocysteine, and N-acetyl-L-cysteine have the capacity to increase thiol content in the lungs. Many synthetic molecules including inhibitors/blockers of protein carbonylation and lipid peroxidation, catalytic antioxidants including superoxide dismutase mimetics, and spin trapping agents can effectively modulate CS-induced OS and its resulting cellular alterations. Several clinical and pre-clinical studies have demonstrated that these antioxidants have the capacity to decrease OS and affect the expressions of several pro-inflammatory genes and genes that are involved with redox and glutathione biosynthesis. In this article, we have summarized the role of OS in COPD pathogenesis. Furthermore, we have particularly focused on the therapeutic potential of numerous chemicals, particularly antioxidants in the treatment of COPD.
Keywords: antioxidants; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD); cigarette smoke; oxidative stress; reactive nitrogen species; reactive oxygen species; small molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological and dietary antioxidant therapies for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Curr Med Chem. 2013;20(12):1496-530. doi: 10.2174/0929867311320120004. Curr Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 22963552 Review.
-
Antioxidant pharmacological therapies for COPD.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2012 Jun;12(3):256-65. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2012.01.015. Epub 2012 Feb 18. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22349417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress and free radicals in COPD--implications and relevance for treatment.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2014 Oct 17;9:1207-24. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S51226. eCollection 2014. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2014. PMID: 25378921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological antioxidant strategies as therapeutic interventions for COPD.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 May;1822(5):714-28. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.11.004. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22101076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of thiols and implications for the use of inhaled corticosteroids in the presence of oxidative stress in COPD.Respir Res. 2023 Jul 31;24(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02500-8. Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 37517999 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative Stress and Air Pollution: Its Impact on Chronic Respiratory Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 3;24(1):853. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010853. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36614301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Molecular Mechanisms and Biomarkers in COPD: An Overview of Current Advancements and Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 4;25(13):7347. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137347. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid metabolism reprogramming in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Mol Med. 2025 Apr 7;31(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01191-9. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40197131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-modal transcriptomic analysis reveals metabolic dysregulation and immune responses in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 30;14(1):22699. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71773-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39349929 Free PMC article.
-
The Promising Effects of Erdosteine and Vitamin B in the Liver Ischemia/Reperfusion Model in Anesthetized Rats.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 May 8;60(5):783. doi: 10.3390/medicina60050783. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38792966 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thimmulappa R.K., Chattopadhyay I., Rajasekaran S. Oxidative stress mechanisms in the pathogenesis of environmental lung diseases. Oxidative Stress Lung Dis. 2019;2:103–137. doi: 10.1007/978-981-32-9366-3_5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

