Newly Designed Quinazolinone Derivatives as Novel Tyrosinase Inhibitor: Synthesis, Inhibitory Activity, and Mechanism
- PMID: 36080324
- PMCID: PMC9457556
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27175558
Newly Designed Quinazolinone Derivatives as Novel Tyrosinase Inhibitor: Synthesis, Inhibitory Activity, and Mechanism
Abstract
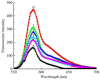
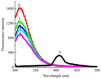
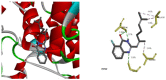
We synthesized a series of quinazolinone derivates as tyrosinase inhibitors and evaluated their inhibition constants. We synthesized 2-(2,6-dimethylhepta-1,5-dien-1-yl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one (Q1) from the natural citral. The concentration, which led to 50% activity loss of Q1, was 103 ± 2 μM (IC50 = 103 ± 2 μM). Furthermore, we considered Q1 to be a mixed-type and reversible tyrosinase inhibitor, and determined the KI and KIS inhibition constants to be 117.07 μM and 423.63 μM, respectively. Our fluorescence experiment revealed that Q1 could interact with the substrates of tyrosine and L-DOPA in addition to tyrosinase. Molecular docking studies showed that the binding of Q1 to tyrosinase was driven by hydrogen bonding and hydrophobicity. Briefly, the current study confirmed a new tyrosinase inhibitor, which is expected to be developed into a novel pigmentation drug.
Keywords: citral; derivatives; fluorescence quenching; inhibitor; molecular docking; tyrosinase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Nunes C.S., Vogel K. General perspectives of enzymes, environment preservation, and scarce natural resources—Conclusions. Enzym. Hum. Anim. Nutr. 2018:515–526. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-805419-2.00027-7. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

