Trends and Technological Advancements in the Possible Food Applications of Spirulina and Their Health Benefits: A Review
- PMID: 36080350
- PMCID: PMC9458102
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27175584
Trends and Technological Advancements in the Possible Food Applications of Spirulina and Their Health Benefits: A Review
Abstract
Spirulina is a kind of blue-green algae (BGA) that is multicellular, filamentous, and prokaryotic. It is also known as a cyanobacterium. It is classified within the phylum known as blue-green algae. Despite the fact that it includes a high concentration of nutrients, such as proteins, vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids-in particular, the necessary omega-3 fatty acids and omega-6 fatty acids-the percentage of total fat and cholesterol that can be found in these algae is substantially lower when compared to other food sources. This is the case even if the percentage of total fat that can be found in these algae is also significantly lower. In addition to this, spirulina has a high concentration of bioactive compounds, such as phenols, phycocyanin pigment, and polysaccharides, which all take part in a number of biological activities, such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. As a result of this, spirulina has found its way into the formulation of a great number of medicinal foods, functional foods, and nutritional supplements. Therefore, this article makes an effort to shed light on spirulina, its nutritional value as a result of its chemical composition, and its applications to some food product formulations, such as dairy products, snacks, cookies, and pasta, that are necessary at an industrial level in the food industry all over the world. In addition, this article supports the idea of incorporating it into the food sector, both from a nutritional and health perspective, as it offers numerous advantages.
Keywords: biological activity; chemical composition; food formulation; functional foods; health and nutritional value; spirulina algae.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

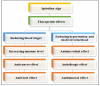
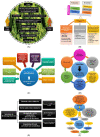
References
-
- Carlson S. Spirulina platensis (Conventional and Organic), Spirulina, Organic Spirulina, or Arthrospira Platensis. Division of Biotechnology and Gras Notice Review, Office of Food Additive Safety-CFSAN; Dauphin Island, AL, USA: 2011. p. 36.
-
- Haoujar I., Haoujar M., Altemimi A.B., Essafi A., Cacciola F. Nutritional, sustainable source of aqua feed and food from microalgae: A mini review. Int. Aquat. Res. 2022;14:1–9.
-
- Singh S., Verma D.K., Thakur M., Tripathy S., Patel A.R., Shah N., Utama G.L., Srivastav P.P., Benavente-Valdés J.R., Chávez-González M.L., et al. Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SCFE) as Green Extraction Technology for High-value Metabolites of Algae, Its Potential Trends in Food and Human Health. Food Res. Int. 2021;150 Pt A:110746. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110746. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nascimento R.Q., Deamici K.M., Tavares P.P.L.G., de Andrade R.B., Guimarães L.C., Costa J.A.V., Guedes K.M., Druzian J.I., de Souza C.O. Improving water kefir nutritional quality via addition of viable Spirulina biomass. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022;17:100914. doi: 10.1016/j.biteb.2021.100914. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

