Extract of Acanthopanax senticosus and Its Components Interacting with Sulfide, Cysteine and Glutathione Increase Their Antioxidant Potencies and Inhibit Polysulfide-Induced Cleavage of Plasmid DNA
- PMID: 36080497
- PMCID: PMC9457693
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27175735
Extract of Acanthopanax senticosus and Its Components Interacting with Sulfide, Cysteine and Glutathione Increase Their Antioxidant Potencies and Inhibit Polysulfide-Induced Cleavage of Plasmid DNA
Abstract
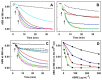
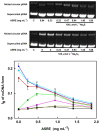
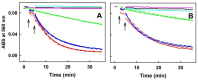
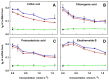
Aqueous root extract from Acanthopanax senticosus (ASRE) has a wide range of medicinal effects. The present work was aimed at studying the influence of sulfide, cysteine and glutathione on the antioxidant properties of ASRE and some of its selected phytochemical components. Reduction of the 2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1H-imidazol-1-yloxy-3-oxide (●cPTIO) stable radical and plasmid DNA (pDNA) cleavage in vitro assays were used to evaluate antioxidant and DNA-damaging properties of ASRE and its individual components. We found that the interaction of ASRE and its two components, caffeic acid and chlorogenic acid (but not protocatechuic acid and eleutheroside B or E), with H2S/HS-, cysteine or glutathione significantly increased the reduction of the ●cPTIO radical. In contrast, the potency of ASRE and its selected components was not affected by Na2S4, oxidized glutathione, cystine or methionine, indicating that the thiol group is a prerequisite for the promotion of the antioxidant effects. ASRE interacting with H2S/HS- or cysteine displayed a bell-shaped effect in the pDNA cleavage assay. However, ASRE and its components inhibited pDNA cleavage induced by polysulfides. In conclusion, we suggest that cysteine, glutathione and H2S/HS- increase antioxidant properties of ASRE and that changes of their concentrations and the thiol/disulfide ratio can influence the resulting biological effects of ASRE.
Keywords: Acanthopanax senticosus; DNA cleavage; H2S; antioxidant; caffeic acid; chlorogenic acid; eleutheroside; polysulfides; radical; ●cPTIO.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures





References
-
- Li X., Chen C., Leng A., Qu J. Advances in the Extraction, Purification, Structural Characteristics and Biological Activities of Eleutherococcus senticosus Polysaccharides: A Promising Medicinal and Edible Resource with Development Value. Front. Pharmacol. 2021;12:753007. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.753007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vaško L., Vašková J., Fejerčáková A., Mojžišová G., Poráčová J. Comparison of some antioxidant properties of plant extracts from Origanum vulgare, Salvia officinalis, Eleutherococcus senticosus and Stevia rebaudiana. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2014;50:614–622. doi: 10.1007/s11626-014-9751-4. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

