Workshop Safety Helmet Wearing Detection Model Based on SCM-YOLO
- PMID: 36081161
- PMCID: PMC9460346
- DOI: 10.3390/s22176702
Workshop Safety Helmet Wearing Detection Model Based on SCM-YOLO
Abstract
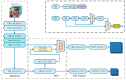
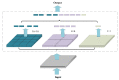
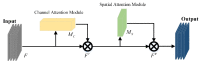
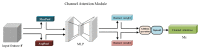
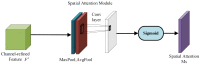
In order to overcome the problems of object detection in complex scenes based on the YOLOv4-tiny algorithm, such as insufficient feature extraction, low accuracy, and low recall rate, an improved YOLOv4-tiny safety helmet-wearing detection algorithm SCM-YOLO is proposed. Firstly, the Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP) structure is added after the backbone network of the YOLOv4-tiny model to improve its adaptability of different scale features and increase its effective features extraction capability. Secondly, Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM), Mish activation function, K-Means++ clustering algorithm, label smoothing, and Mosaic data enhancement are introduced to improve the detection accuracy of small objects while ensuring the detection speed. After a large number of experiments, the proposed SCM-YOLO algorithm achieves a mAP of 93.19%, which is 4.76% higher than the YOLOv4-tiny algorithm. Its inference speed reaches 22.9FPS (GeForce GTX 1050Ti), which meets the needs of the real-time and accurate detection of safety helmets in complex scenes.
Keywords: K-Means++ clustering algorithm; YOLOv4-tiny; convolutional block attention module; label smoothing; safety helmet wearing detection; spatial pyramid pooling structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Research on application of helmet wearing detection improved by YOLOv4 algorithm.Math Biosci Eng. 2023 Mar 6;20(5):8685-8707. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2023381. Math Biosci Eng. 2023. PMID: 37161217
-
Research of Maritime Object Detection Method in Foggy Environment Based on Improved Model SRC-YOLO.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Oct 13;22(20):7786. doi: 10.3390/s22207786. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36298136 Free PMC article.
-
Research on Safety Helmet Detection Algorithm Based on Improved YOLOv5s.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 22;23(13):5824. doi: 10.3390/s23135824. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37447673 Free PMC article.
-
Nature-Inspired Search Method and Custom Waste Object Detection and Classification Model for Smart Waste Bin.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Aug 18;22(16):6176. doi: 10.3390/s22166176. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015936 Free PMC article.
-
An improved YOLO Nano model for dorsal hand vein detection system.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022 May;60(5):1225-1237. doi: 10.1007/s11517-022-02551-x. Epub 2022 Mar 27. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022. PMID: 35347563 Review.
Cited by
-
Improved YOLOv4-tiny based on attention mechanism for skin detection.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2023 Mar 10;9:e1288. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1288. eCollection 2023. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2023. PMID: 37346516 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Recognition of Coal Miners' Unsafe Behavior and Status in the Hoist Cage Based on Machine Vision.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Oct 28;23(21):8794. doi: 10.3390/s23218794. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37960492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Le N., Rathour V.S., Yamazaki K., Luu K., Savvides M. Deep reinforcement learning in computer vision: A comprehensive survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021;55:2733–2819. doi: 10.1007/s10462-021-10061-9. - DOI
-
- Yue S., Zhang Q., Shao D., Fan Y., Bai J. Safety helmet wearing status detection based on improved boosted random ferns. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022;81:16783–16796. doi: 10.1007/s11042-022-12014-y. - DOI
-
- Gu Y., Wang Y., Shi L., Li N., Zhuang L., Xu S. Automatic detection of safety helmet wearing based on head region location. IET Image Process. 2021;15:2441–2453. doi: 10.1049/ipr2.12231. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

